
- 实体框架教程
- 实体框架 - 主页
- 实体框架 - 概述
- 实体框架 - 架构
- 实体 F - 环境设置
- 实体框架 - 数据库设置
- 实体框架 - 数据模型
- 实体框架-DbContext
- 实体框架 - 类型
- 实体框架 - 关系
- 实体框架 - 生命周期
- 实体 F - 代码优先方法
- 实体 F - 模型优先方法
- 实体 F - 数据库优先方法
- 实体框架 - DEV 方法
- 实体F——数据库操作
- 实体框架 - 并发
- 实体框架 - 事务
- 实体框架 - 视图
- 实体框架 - 索引
- 实体 F - 存储过程
- 实体 F - 断开连接的实体
- 实体 F - 表值函数
- 实体框架 - 本机 SQL
- 实体框架 - 枚举支持
- 实体F - 异步查询
- 实体框架 - 持久性
- 实体 F - 投影查询
- 实体 F - 命令记录
- 实体F——命令拦截
- 实体框架 - 空间数据类型
- 实体框架 - 继承
- 实体框架 - 迁移
- 实体框架 - 预加载
- 实体框架 - 延迟加载
- 实体框架 - 显式加载
- 实体框架 - 验证
- 实体框架 - 跟踪更改
- 实体框架 - 彩色实体
- 实体 F - 代码优先方法
- 实体框架 - 第一个示例
- 实体框架 - 数据注释
- 实体框架 - 流畅的 API
- 实体框架-种子数据库
- 实体 F - 代码优先迁移
- 实体 F - 多个 DbContext
- 实体 F - 嵌套实体类型
- 实体框架资源
- 实体框架 - 快速指南
- 实体框架 - 有用的资源
- 实体框架 - 讨论
实体框架 - 多个 DbContext
在本章中,我们将学习当应用程序中有多个 DbContext 类时如何将更改迁移到数据库中。
- 多个 DbContext 首次在 Entity Framework 6.0 中引入。
- 多个上下文类可能属于单个数据库或两个不同的数据库。
在我们的示例中,我们将为同一个数据库定义两个 Context 类。在以下代码中,有两个用于 Student 和 Teacher 的 DbContext 类。
public class Student {
public int ID { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string FirstMidName { get; set; }
public DateTime EnrollmentDate { get; set; }
}
public class MyStudentContext : DbContext {
public MyStudentContext() : base("UniContextDB") {}
public virtual DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
}
public class Teacher {
public int ID { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string FirstMidName { get; set; }
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; }
}
public class MyTeacherContext : DbContext {
public MyTeacherContext() : base("UniContextDB") {}
public virtual DbSet<Teacher> Teachers { get; set; }
}
正如您在上面的代码中看到的,有两个模型,分别称为“学生”和“教师”。每一个都与特定的相应上下文类相关联,即,Student 与 MyStudentContext 相关联,Teacher 与 MyTeacherContext 相关联。
这是当同一项目中有多个 Context 类时迁移数据库中的更改的基本规则。
启用迁移 -ContextTypeName <DbContext-Name-with-Namespaces> MigrationsDirectory:<Migrations-Directory-Name>
Add-Migration -configuration <DbContext-Migrations-Configuration-Class-withNamespaces> <Migrations-Name>
更新数据库-configuration <DbContext-Migrations-Configuration-Class-withNamespaces> -Verbose
让我们通过在包管理器控制台中执行以下命令来启用 MyStudentContext 的迁移。
PM→ enable-migrations -ContextTypeName:EFCodeFirstDemo.MyStudentContext
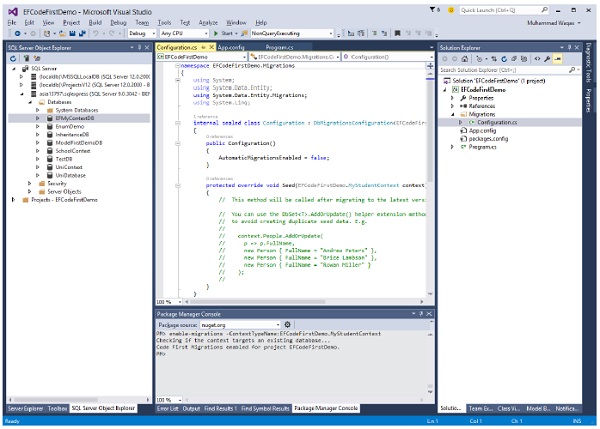
执行后,我们将在迁移历史记录中添加模型,为此,我们必须在同一控制台中触发 add-migration 命令。
PM→ add-migration -configuration EFCodeFirstDemo.Migrations.Configuration Initial
现在让我们将一些数据添加到数据库的学生和教师表中。
static void Main(string[] args) {
using (var context = new MyStudentContext()) {
//// Create and save a new Students
Console.WriteLine("Adding new students");
var student = new Student {
FirstMidName = "Alain",
LastName = "Bomer",
EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Today.ToString())
//Age = 24
};
context.Students.Add(student);
var student1 = new Student {
FirstMidName = "Mark",
LastName = "Upston",
EnrollmentDate = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Today.ToString())
//Age = 30
};
context.Students.Add(student1);
context.SaveChanges();
// Display all Students from the database
var students = (from s in context.Students orderby s.FirstMidName
select s).ToList<Student>();
Console.WriteLine("Retrieve all Students from the database:");
foreach (var stdnt in students) {
string name = stdnt.FirstMidName + " " + stdnt.LastName;
Console.WriteLine("ID: {0}, Name: {1}", stdnt.ID, name);
}
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
using (var context = new MyTeacherContext()) {
//// Create and save a new Teachers
Console.WriteLine("Adding new teachers");
var student = new Teacher {
FirstMidName = "Alain",
LastName = "Bomer",
HireDate = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Today.ToString())
//Age = 24
};
context.Teachers.Add(student);
var student1 = new Teacher {
FirstMidName = "Mark",
LastName = "Upston",
HireDate = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Today.ToString())
//Age = 30
};
context.Teachers.Add(student1);
context.SaveChanges();
// Display all Teachers from the database
var teachers = (from t in context.Teachers orderby t.FirstMidName
select t).ToList<Teacher>();
Console.WriteLine("Retrieve all teachers from the database:");
foreach (var teacher in teachers) {
string name = teacher.FirstMidName + " " + teacher.LastName;
Console.WriteLine("ID: {0}, Name: {1}", teacher.ID, name);
}
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
执行上述代码时,您将看到为两个不同的模型创建了两个不同的表,如下图所示。
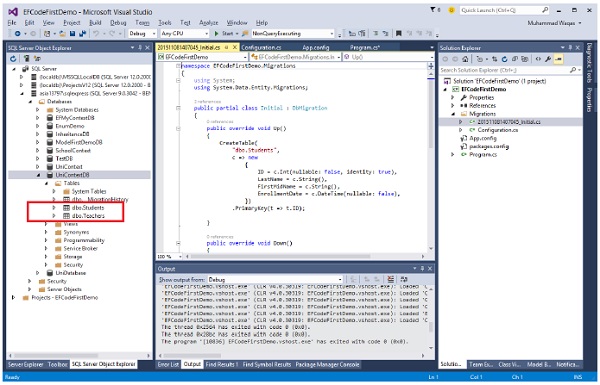
我们建议您逐步执行上述示例,以便更好地理解。