KDB+ - 快速指南
KDB+ - 概述
这是从 kx 系统到kdb+的完整指南,主要针对那些独立学习的人。kdb+于2003年推出,是新一代的kdb数据库,旨在捕获、分析、比较和存储数据。
kdb+ 系统包含以下两个组件 -
KDB+ - 数据库(k 数据库加)
Q - 使用 kdb+ 的编程语言
kdb+和q都是用k 编程语言编写的(与q相同,但可读性较差)。
背景
Kdb+/q 最初是一种晦涩的学术语言,但多年来,它逐渐提高了用户友好性。
APL(1964 年,一种编程语言)
A+(1988 年,由 Arthur Whitney 修改 APL)
K(1993 年,A+ 的清晰版本,由 A. Whitney 开发)
Kdb(1998,内存中基于列的数据库)
Kdb+/q(2003,q 语言 – k 的更可读版本)
为什么以及在哪里使用 KDB+
为什么?− 如果您需要一个用于分析实时数据的单一解决方案,那么您应该考虑 kdb+。Kdb+将数据库作为普通的本机文件存储,因此它对硬件和存储架构没有任何特殊需求。值得指出的是,数据库只是一组文件,因此您的管理工作不会很困难。
在哪里使用 KDB+ ?− 很容易统计哪些投资银行没有使用 kdb+,因为大多数投资银行当前正在使用或计划从传统数据库切换到 kdb+。随着数据量日益增加,我们需要一个能够处理海量数据的系统。KDB+ 满足了这一要求。KDB+不仅存储大量数据,而且还可以实时分析数据。
入门
有了这么多背景知识,现在让我们阐述并学习如何为 KDB+ 设置环境。我们将从如何下载和安装 KDB+ 开始。
下载并安装 KDB+
您可以从http://kx.com/software-download.php获取免费的 32 位版本的 KDB+,其中包含 64 位版本的所有功能
同意许可协议,选择操作系统(适用于所有主流操作系统)。对于Windows操作系统,最新版本是3.2。下载最新版本。解压后,您将获得文件夹名称“windows”,在 windows 文件夹中,您将获得另一个文件夹“q”。将整个q文件夹复制到您的 c:/ 驱动器上。
打开运行终端,输入存储q文件夹的位置;它就像“c:/q/w32/q.exe”。一旦你按下 Enter 键,你将得到一个新的控制台,如下所示 -
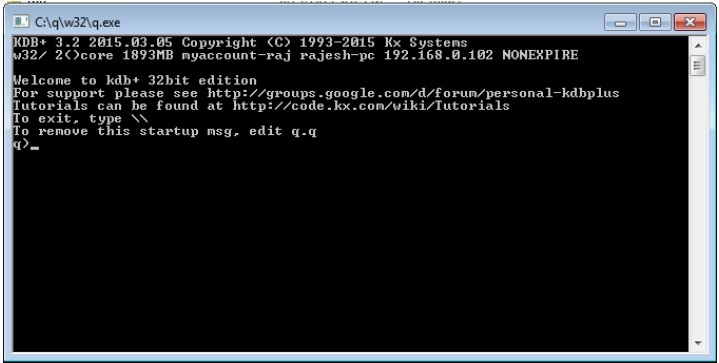
在第一行,您可以看到版本号为 3.2,发布日期为 2015.03.05
目录布局
试用/免费版本一般安装在目录中,
对于 Linux/Mac -
~/q / main q directory (under the user’s home) ~/q/l32 / location of linux 32-bit executable ~/q/m32 / Location of mac 32-bit executable
对于 Windows -
c:/q / Main q directory c:/q/w32/ / Location of windows 32-bit executable
示例文件 -
下载 kdb+ 后,Windows 平台中的目录结构将如下所示 -
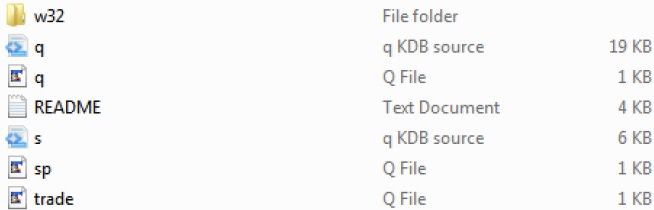
在上面的目录结构中,trade.q和sp.q是我们可以用作参考点的示例文件。
KDB+ - 架构
Kdb+ 是一种高性能、大容量数据库,从一开始就设计用于处理大量数据。它是完全 64 位的,并且具有内置的多核处理和多线程。实时数据和历史数据使用相同的架构。该数据库采用了自己强大的查询语言q,因此可以直接对数据运行分析。
kdb+tick是一种允许捕获、处理和查询实时和历史数据的架构。
Kdb+/tick架构
下图提供了典型 Kdb+/tick 架构的概括轮廓,随后简要说明了各个组件和数据的流通流。
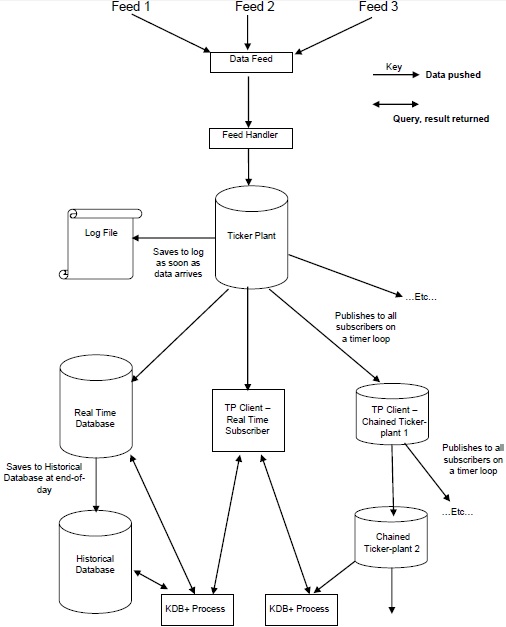
数据源是时间序列数据,主要由路透社、彭博社等数据源提供商或直接从交易所提供。
为了获取相关数据,来自数据馈送的数据由馈送处理程序进行解析。
一旦数据被 feed handler 解析,它就会被发送到ticker-plant。
为了从任何故障中恢复数据,股票代码工厂首先将新数据更新/存储到日志文件中,然后更新其自己的表。
更新内表和日志文件后,实时循环数据将持续发送/发布到实时数据库和所有请求数据的链式订阅者。
在一个工作日结束时,日志文件将被删除,创建一个新的日志文件,并将实时数据库保存到历史数据库中。一旦所有数据都保存到历史数据库中,实时数据库就会清除其表。
Kdb+ Tick 架构的组件
数据源
数据源可以是任何市场或其他时间序列数据。将数据馈送视为馈送处理程序的原始输入。提要可以直接来自交易所(实时流数据)、来自汤森路透、彭博社等新闻/数据提供商或任何其他外部机构。
饲料处理机
提要处理程序将数据流转换为适合写入 kdb+ 的格式。它连接到数据源,检索数据并将其从特定于源的格式转换为 Kdb+ 消息,该消息发布到代码工厂进程。通常,进给处理程序用于执行以下操作 -
- 根据一组规则捕获数据。
- 将数据从一种格式转换(/丰富)为另一种格式。
- 捕获最新值。
股票行情工厂
Ticker Plant 是 KDB+ 架构中最重要的组成部分。它是实时数据库或直接订阅者(客户端)连接以访问财务数据的股票代码工厂。它以发布和订阅机制运行。一旦您获得订阅(许可证),就会定义发布者(股票代码工厂)的蜱(例行)发布。它执行以下操作 -
从 feed 处理程序接收数据。
在代码工厂收到数据后,它会立即将副本存储为日志文件,并在代码工厂获得任何更新后更新它,以便在发生任何故障时,我们不应该丢失任何数据。
客户(实时订阅者)可以直接订阅股票行情。
在每个工作日结束时,即实时数据库收到最后一条消息后,会将当天的所有数据存储到历史数据库中,并将其推送给所有订阅了当天数据的订阅者。然后它重置所有表。一旦数据存储在历史数据库或其他直接链接到实时数据库(rtdb)的订阅者中,日志文件也会被删除。
因此,股票代码工厂、实时数据库和历史数据库可以 24/7 全天候运行。
由于ticker-plant 是一个Kdb+ 应用程序,因此可以像任何其他Kdb+ 数据库一样使用q查询其表。所有代码工厂客户端只能作为订户访问数据库。
实时数据库
实时数据库 (rdb) 存储当前的数据。它直接连接到股票代码工厂。通常,它会在市场交易时段(一天)存储在内存中,并在一天结束时写入历史数据库 (hdb)。由于数据(rdb数据)存储在内存中,处理速度非常快。
由于 kdb+ 建议 RAM 大小为每天预期数据大小的四倍或更多,因此在 rdb 上运行的查询速度非常快,并提供卓越的性能。由于实时数据库仅包含今天的数据,因此不需要日期列(参数)。
例如,我们可以进行 RDB 查询,例如:
select from trade where sym = `ibm OR select from trade where sym = `ibm, price > 100
历史数据库
如果我们必须计算一家公司的估值,我们需要获得其历史数据。历史数据库 (hdb) 保存过去完成的交易数据。每一天的记录都会在一天结束时添加到 HDB。hdb 中的大型表要么以展开方式存储(每列存储在其自己的文件中),要么按时态数据分区存储。此外,一些非常大的数据库可以使用par.txt (文件)进一步分区。
这些存储策略(展开、分区等)在从大型表中搜索或访问数据时非常高效。
历史数据库还可用于内部和外部报告目的,即用于分析。例如,假设我们想要从交易(或任何)表名称中获取 IBM 公司在特定日期的交易,我们需要编写如下查询 -
thisday: 2014.10.12 select from trade where date = thisday, sym =`ibm
注意- 一旦我们了解了q语言的一些概述,我们将编写所有此类查询。
Q 编程语言
Kdb+ 附带其内置编程语言q。它包含标准 SQL 的超集,该超集针对时间序列分析进行了扩展,并比标准版本提供了许多优势。任何熟悉 SQL 的人都可以在几天内学会q并能够快速编写自己的即席查询。
启动“q”环境
要开始使用 kdb+,您需要启动q会话。有三种方法可以启动q会话 -
只需在运行终端上输入“c:/q/w32/q.exe”即可。
启动 MS-DOS 命令终端并输入q。
将q.exe文件复制到“C:\Windows\System32”,然后在运行终端上键入“q”。
这里我们假设您正在 Windows 平台上工作。
数据类型
下表提供了支持的数据类型的列表 -
| 姓名 | 例子 | 查尔 | 类型 | 尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 布尔值 | 1b | 乙 | 1 | 1 |
| 字节 | 0xff | X | 4 | 1 |
| 短的 | 23小时 | H | 5 | 2 |
| 整数 | 23i | 我 | 6 | 4 |
| 长的 | 23j | j | 7 | 8 |
| 真实的 | 2.3e | e | 8 | 4 |
| 漂浮 | 2.3f | F | 9 | 8 |
| 字符 | “A” | C | 10 | 1 |
| varchar | `ab | s | 11 | * |
| 月 | 2003.03m | 米 | 13 | 4 |
| 日期 | 2015.03.17T18:01:40.134 | z | 15 | 8 |
| 分钟 | 08:31 | 你 | 17 号 | 4 |
| 第二 | 08:31:53 | v | 18 | 4 |
| 时间 | 18:03:18.521 | t | 19 | 4 |
| 枚举 | `u$`b,其中 u:`a`b | * | 20 | 4 |
Atomics和列表形成
Atomics是单个实体,例如单个数字、字符或符号。在上表(不同数据类型)中,所有支持的数据类型都是Atomics。列表是Atomics序列或包括列表的其他类型。
将任何类型的Atomics传递给单子(即单参数函数)类型函数将返回负值,即–n,而将这些Atomics的简单列表传递给类型函数将返回正值n。
示例 1 – Atomics和列表形成
/ Note that the comments begin with a slash “ / ” and cause the parser / to ignore everything up to the end of the line. x: `mohan / `mohan is a symbol, assigned to a variable x type x / let’s check the type of x -11h / -ve sign, because it’s single element. y: (`abc;`bca;`cab) / list of three symbols, y is the variable name. type y 11h / +ve sign, as it contain list of atoms (symbol). y1: (`abc`bca`cab) / another way of writing y, please note NO semicolon y2: (`$”symbols may have interior blanks”) / string to symbol conversion y[0] / return `abc y 0 / same as y[0], also returns `abc y 0 2 / returns `abc`cab, same as does y[0 2] z: (`abc; 10 20 30; (`a`b); 9.9 8.8 7.7) / List of different types, z 2 0 / returns (`a`b; `abc), z[2;0] / return `a. first element of z[2] x: “Hello World!” / list of character, a string x 4 0 / returns “oH” i.e. 4th and 0th(first) element
Q 语言 - 类型转换
通常需要将某些数据的数据类型从一种类型更改为另一种类型。标准转换函数是“$”二元运算符。
三种方法用于从一种类型转换为另一种类型(字符串除外) -
- 通过符号名称指定所需的数据类型
- 通过其字符指定所需的数据类型
- 通过短值指定所需的数据类型。
将整数转换为浮点数
在以下将整数转换为浮点数的示例中,所有三种不同的转换方式都是等效的 -
q)a:9 18 27 q)$[`float;a] / Specify desired data type by its symbol name, 1st way 9 18 27f q)$["f";a] / Specify desired data type by its character, 2nd way 9 18 27f q)$[9h;a] / Specify desired data type by its short value, 3rd way 9 18 27f
检查所有三个操作是否等效,
q)($[`float;a]~$["f";a]) and ($[`float;a] ~ $[9h;a]) 1b
将字符串转换为符号
将字符串转换为符号以及反之亦然的工作方式略有不同。让我们用一个例子来检查一下 -
q)b: ("Hello";"World";"HelloWorld") / define a list of strings
q)b
"Hello"
"World"
"HelloWorld"
q)c: `$b / this is how to cast strings to symbols
q)c / Now c is a list of symbols
`Hello`World`HelloWorld
尝试使用关键字 `symbol 或 11h 将字符串转换为符号将失败并出现类型错误 -
q)b "Hello" "World" "HelloWorld" q)`symbol$b 'type q)11h$b 'type
将字符串转换为非符号
将字符串转换为符号以外的数据类型的完成方式如下:
q)b:900 / b contain single atomic integer
q)c:string b / convert this integer atom to string “900”
q)c
"900"
q)`int $ c / converting string to integer will return the
/ ASCII equivalent of the character “9”, “0” and
/ “0” to produce the list of integer 57, 48 and
/ 48.
57 48 48i
q)6h $ c / Same as above
57 48 48i
q)"i" $ c / Same a above
57 48 48i
q)"I" $ c
900i
因此,要将整个字符串(字符列表)转换为数据类型x的单个Atomics,需要我们将表示数据类型x的大写字母指定为$运算符的第一个参数。如果以任何其他方式指定x的数据类型,则会导致将强制转换应用于字符串的每个字符。
Q 语言 - 时态数据
q语言有许多不同的方式来表示和操作时间数据,例如时间和日期。
日期
kdb+ 中的日期在内部存储为自我们的参考日期为 2000 年 1 月 1 日以来的整数天数。该日期之后的日期在内部存储为正数,而在此日期之前的日期被引用为负数。
默认情况下,日期以“YYYY.MM.DD”格式写入
q)x:2015.01.22 / This is how we write 22nd Jan 2015 q)`int$x / Number of days since 2000.01.01 5500i q)`year$x / Extracting year from the date 2015i q)x.year / Another way of extracting year 2015i q)`mm$x / Extracting month from the date 1i q)x.mm / Another way of extracting month 1i q)`dd$x / Extracting day from the date 22i q)x.dd / Another way of extracting day 22i
可以直接对日期进行算术和逻辑运算。
q)x+1 / Add one day 2015.01.23 q)x-7 / Subtract 7 days 2015.01.15
2000 年 1 月 1 日是星期六。因此,历史上或将来的任何星期六除以 7 时都会产生余数 0,星期日产生 1,星期一产生 2。
Day mod 7
Saturday 0
Sunday 1
Monday 2
Tuesday 3
Wednesday 4
Thursday 5
Friday 6
时代
时间在内部存储为自午夜钟声敲响以来的整数毫秒数。时间以 HH:MM:SS.MSS 格式写入
q)tt1: 03:30:00.000 / tt1 store the time 03:30 AM q)tt1 03:30:00.000 q)`int$tt1 / Number of milliseconds in 3.5 hours 12600000i q)`hh$tt1 / Extract the hour component from time 3i q)tt1.hh 3i q)`mm$tt1 / Extract the minute component from time 30i q)tt1.mm 30i q)`ss$tt1 / Extract the second component from time 0i q)tt1.ss 0i
与日期一样,可以直接对时间进行算术运算。
日期时间
日期时间是日期和时间的组合,按照 ISO 标准格式以“T”分隔。日期时间值存储从 2000 年 1 月 1 日午夜开始的小数天数。
q)dt:2012.12.20T04:54:59:000 / 04:54.59 AM on 20thDec2012 q)type dt -15h q)dt 2012.12.20T04:54:59.000 9 q)`float$dt 4737.205
可以通过转换为浮点来获得基础的小数天数。
Q 语言 - 列表
列表是q语言的基本构建块,因此彻底理解列表非常重要。列表只是Atomics(Atomics元素)和其他列表(一个或多个Atomics的组)的有序集合。
列表类型
通用列表将其项目括在匹配的括号内,并用分号分隔它们。例如 -
(9;8;7) or ("a"; "b"; "c") or (-10.0; 3.1415e; `abcd; "r")
如果一个列表由相同类型的Atomics组成,则称为统一列表。否则,它被称为通用列表(混合类型)。
数数
我们可以通过计数来获取列表中的项目数。
q)l1:(-10.0;3.1415e;`abcd;"r") / Assigning variable name to general list q)count l1 / Calculating number of items in the list l1 4
简单列表的示例
q)h:(1h;2h;255h) / Simple Integer List
q)h
1 2 255h
q)f:(123.4567;9876.543;98.7) / Simple Floating Point List
q)f
123.4567 9876.543 98.7
q)b:(0b;1b;0b;1b;1b) / Simple Binary Lists
q)b
01011b
q)symbols:(`Life;`Is;`Beautiful) / Simple Symbols List
q)symbols
`Life`Is`Beautiful
q)chars:("h";"e";"l";"l";"o";" ";"w";"o";"r";"l";"d")
/ Simple char lists and Strings.
q)chars
"hello world"
**注意 - 简单的字符列表称为字符串。
列表包含Atomics或列表。要创建单个项目列表,我们使用 -
q)singleton:enlist 42 q)singleton ,42
要区分Atomics和等效的单例,请检查它们类型的符号。
q)signum type 42 -1i q)signum type enlist 42 1i
Q 语言 - 索引
列表按其项目的位置从左到右排序。项目相对于列表开头的偏移量称为其索引。因此,第一项的索引为 0,第二项(如果有)的索引为 1,等等。计数为n的列表的索引域为0到n–1。
索引符号
给定一个列表L ,索引i处的项目由L[i]访问。通过索引检索项目称为项目索引。例如,
q)L:(99;98.7e;`b;`abc;"z") q)L[0] 99 q)L[1] 98.7e q)L[4] "z
索引作业
列表中的项目也可以通过项目索引进行分配。因此,
q)L1:9 8 7
q)L1[2]:66 / Indexed assignment into a simple list
/ enforces strict type matching.
q)L1
9 8 66
变量列表
q)l1:(9;8;40;200) q)l2:(1 4 3; `abc`xyz) q)l:(l1;l2) / combining the two list l1 and l2 q)l 9 8 40 200 (1 4 3;`abc`xyz)
加入列表
对两个列表最常见的操作是将它们连接在一起以形成一个更大的列表。更准确地说,连接运算符 (,) 将其右操作数附加到左操作数的末尾并返回结果。它接受任一参数中的一个Atomics。
q)1,2 3 4
1 2 3 4
q)1 2 3, 4.4 5.6 / If the arguments are not of uniform type,
/ the result is a general list.
1
2
3
4.4
5.6
嵌套
数据复杂性是通过使用列表作为列表项来构建的。
深度
列表的嵌套层数称为其深度。Atomics的深度为 0,简单列表的深度为 1。
q)l1:(9;8;(99;88)) q)count l1 3
这是一个深度为 3 的列表,有两个项目 -
q)l5 9 (90;180;900 1800 2700 3600) q)count l5 2 q)count l5[1] 3
深度索引
可以直接索引嵌套列表的项目。
重复项目索引
通过单个索引检索项目始终会从嵌套列表中检索最上面的项目。
q)L:(1;(100;200;(300;400;500;600))) q)L[0] 1 q)L[1] 100 200 300 400 500 600
由于结果L[1]本身就是一个列表,因此我们可以使用单个索引检索其元素。
q)L[1][2] 300 400 500 600
我们可以再次重复单个索引以从最里面的嵌套列表中检索项目。
q)L[1][2][0] 300
您可以将其读作:
从 L 中获取索引 1 处的项目,并从中检索索引 2 处的项目,并从中检索索引 0 处的项目。
深度索引符号
有另一种表示法用于重复索引嵌套列表的组成部分。最后一次检索也可以写成,
q)L[1;2;0] 300
通过索引进行赋值也适用于深度。
q)L[1;2;1]:900 q)L 1 (100;200;300 900 500 600)
消除指数
消除一般列表的索引
q)L:((1 2 3; 4 5 6 7); (`a`b`c;`d`e`f`g;`0`1`2);("good";"morning"))
q)L
(1 2 3;4 5 6 7)
(`a`b`c;`d`e`f`g;`0`1`2)
("good";"morning")
q)L[;1;]
4 5 6 7
`d`e`f`g
"morning"
q)L[;;2]
3 6
`c`f`2
"or"
将 L[;1;] 解释为,
检索顶层每个列表的第二个位置中的所有项目。
将 L[;;2] 解释为,
检索第二级每个列表的第三位置的项目。
Q 语言 - 词典
字典是列表的扩展,为创建表提供了基础。用数学术语来说,字典创建了
“域→范围”
或一般(简短)创建
“键→值”
元素之间的关系。
字典是键值对的有序集合,大致相当于哈希表。字典是由域列表和范围列表之间通过位置对应的显式 I/O 关联定义的映射。字典的创建使用“xkey”原语(!)
ListOfDomain ! ListOfRange
最基本的字典将简单列表映射到简单列表。
| 输入(一) | 输出(O) |
|---|---|
| `名称 | '约翰 |
| `年龄 | 36 |
| `性 | “M” |
| 重量 | 60.3 |
q)d:`Name`Age`Sex`Weight!(`John;36;"M";60.3) / Create a dictionary d q)d Name | `John Age | 36 Sex | "M" Weight | 60.3 q)count d / To get the number of rows in a dictionary. 4 q)key d / The function key returns the domain `Name`Age`Sex`Weight q)value d / The function value returns the range. `John 36 "M" 60.3 q)cols d / The function cols also returns the domain. `Name`Age`Sex`Weight
抬头
查找与输入值对应的字典输出值称为查找输入。
q)d[`Name] / Accessing the value of domain `Name `John q)d[`Name`Sex] / extended item-wise to a simple list of keys `John "M"
用动词@查找
q)d1:`one`two`three!9 18 27 q)d1[`two] 18 q)d1@`two 18
字典操作
修改和更新插入
与列表一样,字典的项目可以通过索引分配进行修改。
d:`Name`Age`Sex`Weight! (`John;36;"M";60.3)
/ A dictionary d
q)d[`Age]:35 / Assigning new value to key Age
q)d
/ New value assigned to key Age in d
Name | `John
Age | 35
Sex | "M"
Weight | 60.3
字典可以通过索引分配来扩展。
q)d[`Height]:"182 Ft" q)d Name | `John Age | 35 Sex | "M" Weight | 60.3 Height | "182 Ft"
使用 Find (?) 进行反向查找
find (?) 运算符用于通过将一系列元素映射到其域元素来执行反向查找。
q)d2:`x`y`z!99 88 77 q)d2?77 `z
如果列表的元素不唯一,则查找返回从域列表映射到它的第一个项目。
删除条目
要从字典中删除条目,请使用删除 (_) 函数。( _ ) 的左操作数是字典,右操作数是键值。
q)d2:`x`y`z!99 88 77 q)d2 _`z x| 99 y| 88
如果第一个操作数是变量,则 _ 左侧需要有空格。
q)`x`y _ d2 / Deleting multiple entries z| 77
专栏词典
列字典是创建表的基础。考虑以下示例 -
q)scores: `name`id!(`John`Jenny`Jonathan;9 18 27)
/ Dictionary scores
q)scores[`name] / The values for the name column are
`John`Jenny`Jonathan
q)scores.name / Retrieving the values for a column in a
/ column dictionary using dot notation.
`John`Jenny`Jonathan
q)scores[`name][1] / Values in row 1 of the name column
`Jenny
q)scores[`id][2] / Values in row 2 of the id column is
27
翻字典
翻转列字典的最终效果只是反转索引的顺序。这在逻辑上相当于调换行和列。
翻转列字典
字典的转置是通过应用一元翻转运算符获得的。看一下下面的例子 -
q)scores name | John Jenny Jonathan id | 9 18 27 q)flip scores name id --------------- John 9 Jenny 18 Jonathan 27
翻转列字典的翻转
如果你将字典转置两次,你将得到原始字典,
q)scores ~ flip flip scores 1b
Q 语言 - 表格
表是 kdb+ 的核心。表是作为字典实现的命名列的集合。q 表是面向列的。
创建表
表是使用以下语法创建的 -
q)trade:([]time:();sym:();price:();size:()) q)trade time sym price size -------------------
在上面的例子中,我们没有指定每一列的类型。这将由第一次插入表中时设置。
另一种方法,我们可以在初始化时指定列类型 -
q)trade:([]time:`time$();sym:`$();price:`float$();size:`int$())
或者我们也可以定义非空表 -
q)trade:([]sym:(`a`b);price:(1 2)) q)trade sym price ------------- a 1 b 2
如果方括号内没有列(如上面的示例所示),则该表未加键。
要创建键表,我们将键的列插入方括号中。
q)trade:([sym:`$()]time:`time$();price:`float$();size:`int$()) q)trade sym | time price size ----- | ---------------
还可以通过将值设置为各种类型的空列表来定义列类型 -
q)trade:([]time:0#0Nt;sym:0#`;price:0#0n;size:0#0N)
获取表信息
让我们创建一个交易表 -
trade: ([]sym:`ibm`msft`apple`samsung;mcap:2000 4000 9000 6000;ex:`nasdaq`nasdaq`DAX`Dow) q)cols trade / column names of a table `sym`mcap`ex q)trade.sym / Retrieves the value of column sym `ibm`msft`apple`samsung q)show meta trade / Get the meta data of a table trade. c | t f a ----- | ----- Sym | s Mcap | j ex | s
主键和键控表
带钥匙的桌子
键控表是一个字典,它将唯一键表中的每一行映射到值表中的相应行。让我们举个例子 -
val:flip `name`id!(`John`Jenny`Jonathan;9 18 27)
/ a flip dictionary create table val
id:flip (enlist `eid)!enlist 99 198 297
/ flip dictionary, having single column eid
现在创建一个简单的键控表,其中包含 eid 作为键,
q)valid: id ! val q)valid / table name valid, having key as eid eid | name id --- | --------------- 99 | John 9 198 | Jenny 18 297 | Jonathan 27
外键
外键定义从定义它的表的行到具有相应主键的表的行的映射。
外键提供引用完整性。换句话说,尝试插入不在主键中的外键值将会失败。
考虑以下示例。在第一个示例中,我们将在初始化时显式定义外键。在第二个示例中,我们将使用外键追踪,它不假设两个表之间有任何先前关系。
示例 1 - 在初始化时定义外键
q)sector:([sym:`SAMSUNG`HSBC`JPMC`APPLE]ex:`N`CME`DAQ`N;MC:1000 2000 3000 4000) q)tab:([]sym:`sector$`HSBC`APPLE`APPLE`APPLE`HSBC`JPMC;price:6?9f) q)show meta tab c | t f a ------ | ---------- sym | s sector price | f q)show select from tab where sym.ex=`N sym price ---------------- APPLE 4.65382 APPLE 4.643817 APPLE 3.659978
示例 2 - 表之间没有预定义的关系
sector: ([symb:`IBM`MSFT`HSBC]ex:`N`CME`N;MC:1000 2000 3000) tab:([]sym:`IBM`MSFT`MSFT`HSBC`HSBC;price:5?9f)
要使用外键追踪,我们必须创建一个表来键入扇区。
q)show update mc:(sector([]symb:sym))[`MC] from tab sym price mc -------------------------- IBM 7.065297 1000 MSFT 4.812387 2000 MSFT 6.400545 2000 HSBC 3.704373 3000 HSBC 4.438651 3000
预定义外键的一般符号 -
select ab from c其中 a 是外键 (sym),b 是 a
主键表 (ind) 中的字段,c 是
外键表(贸易)
操作表格
让我们创建一个交易表并检查不同表表达式的结果 -
q)trade:([]sym:5?`ibm`msft`hsbc`samsung;price:5?(303.00*3+1);size:5?(900*5);time:5?(.z.T-365)) q)trade sym price size time ----------------------------------------- msft 743.8592 3162 02:32:17.036 msft 641.7307 2917 01:44:56.936 hsbc 838.2311 1492 00:25:23.210 samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 838.6471 4006 07:24:26.842
现在让我们看一下使用q语言操作表的语句。
选择
使用Select语句的语法如下 -
select [columns] [by columns] from table [where clause]
现在让我们举一个例子来演示如何使用 Select 语句 -
q)/ select expression example
q)select sym,price,size by time from trade where size > 2000
time | sym price size
------------- | -----------------------
01:44:56.936 | msft 641.7307 2917
02:32:17.036 | msft 743.8592 3162
07:24:26.842 | ibm 838.6471 4006
插入
使用Insert语句的语法如下 -
`tablename insert (values) Insert[`tablename; values]
现在让我们举一个例子来演示如何使用 Insert 语句 -
q)/ Insert expression example q)`trade insert (`hsbc`apple;302.0 730.40;3020 3012;09:30:17.00409:15:00.000) 5 6 q)trade sym price size time ------------------------------------------ msft 743.8592 3162 02:32:17.036 msft 641.7307 2917 01:44:56.936 hsbc 838.2311 1492 00:25:23.210 samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 838.6471 4006 07:24:26.842 hsbc 302 3020 09:30:17.004 apple 730.4 3012 09:15:00.000 q)/Insert another value q)insert[`trade;(`samsung;302.0; 3333;10:30:00.000] '] q)insert[`trade;(`samsung;302.0; 3333;10:30:00.000)] ,7 q)trade sym price size time ---------------------------------------- msft 743.8592 3162 02:32:17.036 msft 641.7307 2917 01:44:56.936 hsbc 838.2311 1492 00:25:23.210 samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 838.6471 4006 07:24:26.842 hsbc 302 3020 09:30:17.004 apple 730.4 3012 09:15:00.000 samsung 302 3333 10:30:00.000
删除
使用删除语句的语法如下 -
delete columns from table delete from table where clause
现在让我们举一个例子来演示如何使用删除语句 -
q)/Delete expression example q)delete price from trade sym size time ------------------------------- msft 3162 02:32:17.036 msft 2917 01:44:56.936 hsbc 1492 00:25:23.210 samsung 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 4006 07:24:26.842 hsbc 3020 09:30:17.004 apple 3012 09:15:00.000 samsung 3333 10:30:00.000 q)delete from trade where price > 3000 sym price size time ------------------------------------------- msft 743.8592 3162 02:32:17.036 msft 641.7307 2917 01:44:56.936 hsbc 838.2311 1492 00:25:23.210 samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 838.6471 4006 07:24:26.842 hsbc 302 3020 09:30:17.004 apple 730.4 3012 09:15:00.000 samsung 302 3333 10:30:00.000 q)delete from trade where price > 500 sym price size time ----------------------------------------- samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 hsbc 302 3020 09:30:17.004 samsung 302 3333 10:30:00.000
更新
使用Update语句的语法如下 -
update column: newValue from table where ….
使用以下语法通过转换函数更新列的格式/数据类型 -
update column:newValue from `table where …
现在让我们举个例子来演示如何使用Update语句 -
q)/Update expression example q)update size:9000 from trade where price > 600 sym price size time ------------------------------------------ msft 743.8592 9000 02:32:17.036 msft 641.7307 9000 01:44:56.936 hsbc 838.2311 9000 00:25:23.210 samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 838.6471 9000 07:24:26.842 hsbc 302 3020 09:30:17.004 apple 730.4 9000 09:15:00.000 samsung 302 3333 10:30:00.000 q)/Update the datatype of a column using the cast function q)meta trade c | t f a ----- | -------- sym | s price| f size | j time | t q)update size:`float$size from trade sym price size time ------------------------------------------ msft 743.8592 3162 02:32:17.036 msft 641.7307 2917 01:44:56.936 hsbc 838.2311 1492 00:25:23.210 samsung 278.3498 1983 00:29:38.945 ibm 838.6471 4006 07:24:26.842 hsbc 302 3020 09:30:17.004 apple 730.4 3012 09:15:00.000 samsung 302 3333 10:30:00.000 q)/ Above statement will not update the size column datatype permanently q)meta trade c | t f a ------ | -------- sym | s price | f size | j time | t q)/to make changes in the trade table permanently, we have do q)update size:`float$size from `trade `trade q)meta trade c | t f a ------ | -------- sym | s price | f size | f time | t
Q Language - 动词和副词
Kdb+ 有名词、动词和副词。所有数据对象和函数都是名词。动词通过减少表达式中方括号和圆括号的数量来增强可读性。副词修饰二元(2 个参数)功能和动词以产生新的相关动词。副词产生的功能称为派生功能或派生动词。
每个
由 ( ` ) 表示的副词every修饰二元函数和动词以应用于列表项而不是列表本身。看一下下面的例子 -
q)1, (2 3 5) / Join 1 2 3 5 q)1, '( 2 3 4) / Join each 1 2 1 3 1 4
单子函数有一种使用关键字“each”的Each形式。例如,
q)reverse ( 1 2 3; "abc") /Reverse a b c 1 2 3 q)each [reverse] (1 2 3; "abc") /Reverse-Each 3 2 1 c b a q)'[reverse] ( 1 2 3; "abc") 3 2 1 c b a
每个左和每个右
二元函数的 Each 有两种变体,称为Each-Left (\:) 和Each-Right (/:)。以下示例解释了如何使用它们。
q)x: 9 18 27 36
q)y:10 20 30 40
q)x,y / join
9 18 27 36 10 20 30 40
q)x,'y / each
9 10
18 20
27 30
36 40
q)x: 9 18 27 36
q)y:10 20 30 40
q)x,y / join
9 18 27 36 10 20 30 40
q)x,'y / each, will return a list of pairs
9 10
18 20
27 30
36 40
q)x, \:y / each left, returns a list of each element
/ from x with all of y
9 10 20 30 40
18 10 20 30 40
27 10 20 30 40
36 10 20 30 40
q)x,/:y / each right, returns a list of all the x with
/ each element of y
9 18 27 36 10
9 18 27 36 20
9 18 27 36 30
9 18 27 36 40
q)1 _x / drop the first element
18 27 36
q)-2_y / drop the last two element
10 20
q) / Combine each left and each right to be a
/ cross-product (cartesian product)
q)x,/:\:y
9 10 9 20 9 30 9 40
18 10 18 20 18 30 18 40
27 10 27 20 27 30 27 40
36 10 36 20 36 30 36 40
Q 语言 - 连接
在q语言中,我们根据提供的输入表和我们想要的连接表类型有不同类型的连接。连接合并两个表中的数据。除了外键追踪之外,还有四种连接表的方法 -
- 简单连接
- 阿索夫加盟
- 左连接
- 联盟加入
在本章中,我们将详细讨论每个连接。
简单加入
简单连接是最基本的连接类型,使用逗号“,”执行。在这种情况下,两个表必须类型一致,即两个表具有相同顺序的相同列数和相同的键。
table1,:table2 / table1 is assigned the value of table2
对于相同长度的表,我们可以使用逗号每个连接来横向连接。其中一张表可以在此处键入,
Table1, `Table2
Asof 加入 (aj)
它是最强大的联接,用于获取一个表中的字段在另一个表中的时间值。一般用于获取每次交易时的现行买价和卖价。
通用格式
aj[joinColumns;tbl1;tbl2]
例如,
aj[`sym`time;trade;quote]
例子
q)tab1:([]a:(1 2 3 4);b:(2 3 4 5);d:(6 7 8 9)) q)tab2:([]a:(2 3 4);b:(3 4 5); c:( 4 5 6)) q)show aj[`a`b;tab1;tab2] a b d c ------------- 1 2 6 2 3 7 4 3 4 8 5 4 5 9 6
左连接(lj)
这是 aj 的特殊情况,其中第二个参数是键控表,第一个参数包含右侧参数的键的列。
通用格式
table1 lj Keyed-table
例子
q)/Left join- syntax table1 lj table2 or lj[table1;table2] q)tab1:([]a:(1 2 3 4);b:(2 3 4 5);d:(6 7 8 9)) q)tab2:([a:(2 3 4);b:(3 4 5)]; c:( 4 5 6)) q)show lj[tab1;tab2] a b d c ------------- 1 2 6 2 3 7 4 3 4 8 5 4 5 9 6
联合连接 (uj)
它允许创建具有不同模式的两个表的并集。它基本上是简单连接 ( , ) 的扩展
q)tab1:([]a:(1 2 3 4);b:(2 3 4 5);d:(6 7 8 9)) q)tab2:([]a:(2 3 4);b:(3 4 5); c:( 4 5 6)) q)show uj[tab1;tab2] a b d c ------------ 1 2 6 2 3 7 3 4 8 4 5 9 2 3 4 3 4 5 4 5 6
如果您在带键的表上使用 uj,则主键必须匹配。
Q 语言 - 函数
功能类型
函数可以按多种方式分类。在这里,我们根据它们采用的参数的数量和类型以及结果类型对它们进行了分类。功能可以是,
Atomics- 参数是Atomics的并产生Atomics结果
聚合- 列表中的Atomics
Uniform (list from list) - 扩展了Atomics的概念,因为它们适用于列表。参数列表的计数等于结果列表的计数。
其他- 如果函数不属于上述类别。
数学中的二元运算称为q 中的二元函数;例如,“+”。类似地,一元运算称为一元函数;例如,“abs”或“floor”。
常用功能
q编程中有很多常用的函数。在本节中,我们将看到一些流行函数的用法 -
腹肌
q) abs -9.9 / Absolute value, Negates -ve number & leaves non -ve number 9.9
全部
q) all 4 5 0 -4 / Logical AND (numeric min), returns the minimum value 0b
最大值 (&)、最小值 (|) 和非 (!)
q) /And, Or, and Logical Negation q) 1b & 1b / And (Max) 1b q) 1b|0b / Or (Min) 1b q) not 1b /Logical Negate (Not) 0b
升序
q)asc 1 3 5 7 -2 0 4 / Order list ascending, sorted list
/ in ascending order i
s returned
`s#-2 0 1 3 4 5 7
q)/attr - gives the attributes of data, which describe how it's sorted.
`s denotes fully sorted, `u denotes unique and `p and `g are used to
refer to lists with repetition, with `p standing for parted and `g for grouped
平均
q)avg 3 4 5 6 7 / Return average of a list of numeric values 5f q)/Create on trade table q)trade:([]time:3?(.z.Z-200);sym:3?(`ibm`msft`apple);price:3?99.0;size:3?100)
经过
q)/ by - Groups rows in a table at given sym q)select sum price by sym from trade / find total price for each sym sym | price ------ | -------- apple | 140.2165 ibm | 16.11385
列
q)cols trade / Lists columns of a table `time`sym`price`size
数数
q)count (til 9) / Count list, count the elements in a list and
/ return a single int value 9
港口
q)\p 9999 / assign port number q)/csv - This command allows queries in a browser to be exported to excel by prefixing the query, such as http://localhost:9999/.csv?select from trade where sym =`ibm
切
q)/ cut - Allows a table or list to be cut at a certain point
q)(1 3 5) cut "abcdefghijkl"
/ the argument is split at 1st, 3rd and 5th letter.
"bc"
"de"
"fghijkl"
q)5 cut "abcdefghijkl" / cut the right arg. Into 5 letters part
/ until its end.
"abcde"
"fghij"
"kl"
删除
q)/delete - Delete rows/columns from a table
q)delete price from trade
time sym size
---------------------------------------
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 36
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 12
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 97
清楚的
q)/distinct - Returns the distinct element of a list q)distinct 1 2 3 2 3 4 5 2 1 3 / generate unique set of number 1 2 3 4 5
入伍
q)/enlist - Creates one-item list. q)enlist 37 ,37 q)type 37 / -ve type value -7h q)type enlist 37 / +ve type value 7h
填写 (^)
q)/fill - used with nulls. There are three functions for processing null values. The dyadic function named fill replaces null values in the right argument with the atomic left argument. q)100 ^ 3 4 0N 0N -5 3 4 100 100 -5 q)`Hello^`jack`herry``john` `jack`herry`Hello`john`Hello
填充
q)/fills - fills in nulls with the previous not null value. q)fills 1 0N 2 0N 0N 2 3 0N -5 0N 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 -5 -5
第一的
q)/first - returns the first atom of a list q)first 1 3 34 5 3 1
翻动
q)/flip - Monadic primitive that applies to lists and associations. It interchange the top two levels of its argument.
q)trade
time sym price size
------------------------------------------------------
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 72.05742 36
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 16.11385 12
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 68.15909 97
q)flip trade
time | 2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 2009.11.14T12:42:34.653
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518
sym | apple ibm apple
price | 72.05742 16.11385 68.15909
size | 36 12 97
机构间常设委员会
q)/iasc - Index ascending, return the indices of the ascended sorted list relative to the input list. q)iasc 5 4 0 3 4 9 2 3 1 4 0 5
伊德斯克
q)/idesc - Index desceding, return the descended sorted list relative to the input list q)idesc 0 1 3 4 3 2 1 0
在
q)/in - In a list, dyadic function used to query list (on the right-handside) about their contents. q)(2 4) in 1 2 3 10b
插入
q)/insert - Insert statement, upload new data into a table.
q)insert[`trade;((.z.Z);`samsung;48.35;99)],3
q)trade
time sym price size
------------------------------------------------------
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 72.05742 36
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 16.11385 12
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 68.15909 97
2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 samsung 48.35 99
钥匙
q)/key - three different functions i.e. generate +ve integer number, gives content of a directory or key of a table/dictionary. q)key 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 q)key `:c: `$RECYCLE.BIN`Config.Msi`Documents and Settings`Drivers`Geojit`hiberfil.sys`I..
降低
q)/lower - Convert to lower case and floor
q)lower ("JoHn";`HERRY`SYM)
"john"
`herry`sym
最大值和最小值(即 | 和 &)
q)/Max and Min / a|b and a&b q)9|7 9 q)9&5 5
无效的
q)/null - return 1b if the atom is a null else 0b from the argument list q)null 1 3 3 0N 0001b
桃
q)/peach - Parallel each, allows process across slaves
q)foo peach list1 / function foo applied across the slaves named in list1
'list1
q)foo:{x+27}
q)list1:(0 1 2 3 4)
q)foo peach list1 / function foo applied across the slaves named in list1
27 28 29 30 31
上一篇
q)/prev - returns the previous element i.e. pushes list forwards q)prev 0 1 3 4 5 7 0N 0 1 3 4 5
随机的( ?)
q)/random - syntax - n?list, gives random sequences of ints and floats q)9?5 0 0 4 0 3 2 2 0 1 q)3?9.9 0.2426823 1.674133 3.901671
夷
q)/raze - Flattn a list of lists, removes a layer of indexing from a list of lists. for instance:
q)raze (( 12 3 4; 30 0);("hello";7 8); 1 3 4)
12 3 4
30 0
"hello"
7 8
1
3
4
读0
q)/read0 - Read in a text file q)read0 `:c:/q/README.txt / gives the contents of *.txt file
读1
q)/read1 - Read in a q data file q)read1 `:c:/q/t1 0xff016200630b000500000073796d0074696d6500707269636…
撤销
q)/reverse - Reverse a list q)reverse 2 30 29 1 3 4 4 3 1 29 30 2 q)reverse "HelloWorld" "dlroWolleH"
放
q)/set - set value of a variable
q)`x set 9
`x
q)x
9
q)`:c:/q/test12 set trade
`:c:/q/test12
q)get `:c:/q/test12
time sym price size
---------------------------------------------------------
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 72.05742 36
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 16.11385 12
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 68.15909 97
2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:03:47.540 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:04:44.844 samsung 48.35 99
超导系统
q)/ssr - String search and replace, syntax - ssr["string";searchstring;replaced-with] q)ssr["HelloWorld";"o";"O"] "HellOWOrld"
细绳
q)/string - converts to string, converts all types to a string format. q)string (1 2 3; `abc;"XYZ";0b) (,"1";,"2";,"3") "abc" (,"X";,"Y";,"Z") ,"0"
SV
q)/sv - Scalar from vector, performs different tasks dependent on its arguments. It evaluates the base representation of numbers, which allows us to calculate the number of seconds in a month or convert a length from feet and inches to centimeters. q)24 60 60 sv 11 30 49 41449 / number of seconds elapsed in a day at 11:30:49
系统
q)/system - allows a system command to be sent, q)system "dir *.py" " Volume in drive C is New Volume" " Volume Serial Number is 8CD2-05B2" "" " Directory of C:\\Users\\myaccount-raj" "" "09/14/2014 06:32 PM 22 hello1.py" " 1 File(s) 22 bytes"
桌子
q)/tables - list all tables q)tables ` `s#`tab1`tab2`trade
蒂尔
q)/til - Enumerate q)til 5 0 1 2 3 4
修剪
q)/trim - Eliminate string spaces q)trim " John " "John"
与
q)/vs - Vector from scaler , produces a vector quantity from a scaler quantity q)"|" vs "20150204|msft|20.45" "20150204" "msft" "20.45"
XASC
q)/xasc - Order table ascending, allows a table (right-hand argument) to be sorted such that (left-hand argument) is in ascending order
q)`price xasc trade
time sym price size
----------------------------------------------------------
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 16.11385 12
2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:03:47.540 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:04:44.844 samsung 48.35 99
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 68.15909 97
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 72.05742 36
xcol
q)/xcol - Renames columns of a table
q)`timeNew`symNew xcol trade
timeNew symNew price size
-------------------------------------------------------------
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 72.05742 36
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 16.11385 12
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 68.15909 97
2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:03:47.540 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:04:44.844 samsung 48.35 99
xcols
q)/xcols - Reorders the columns of a table, q)`size`price xcols trade size price time sym ----------------------------------------------------------- 36 72.05742 2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 12 16.11385 2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 97 68.15909 2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 99 48.35 2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 samsung 99 48.35 2015.04.06T10:03:47.540 samsung 99 48.35 2015.04.06T10:04:44.844 samsung
描述
q)/xdesc - Order table descending, allows tables to be sorted such that the left-hand argument is in descending order.
q)`price xdesc trade
time sym price size
-----------------------------------------------------------
2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 apple 72.05742 36
2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 apple 68.15909 97
2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:03:47.540 samsung 48.35 99
2015.04.06T10:04:44.844 samsung 48.35 99
2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 ibm 16.11385 12
x组
q)/xgroup - Creates nested table q)`x xgroup ([]x:9 18 9 18 27 9 9;y:10 20 10 20 30 40) 'length q)`x xgroup ([]x:9 18 9 18 27 9 9;y:10 20 10 20 30 40 10) x | y ---- | ----------- 9 | 10 10 40 10 18 | 20 20 27 | ,30
x键
q)/xkey - Set key on table
q)`sym xkey trade
sym | time price size
--------- | -----------------------------------------------
apple | 2009.06.18T06:04:42.919 72.05742 36
ibm | 2009.11.14T12:42:34.653 16.11385 12
apple | 2009.12.27T17:02:11.518 68.15909 97
samsung | 2015.04.06T10:03:36.738 48.35 99
samsung | 2015.04.06T10:03:47.540 48.35 99
samsung | 2015.04.06T10:04:44.844 48.35 99
系统命令
系统命令控制q环境。它们的形式如下 -
\cmd [p] where p may be optional
下面讨论了一些流行的系统命令 -
\a [命名空间] – 列出给定命名空间中的表
q)/Tables in default namespace q)\a ,`trade q)\a .o / table in .o namespace. ,`TI
\b – 查看依赖关系
q)/ views/dependencies q)a:: x+y / global assingment q)b:: x+1 q)\b `s#`a`b
\B – 待处理的视图/依赖项
q)/ Pending views/dependencies q)a::x+1 / a depends on x q)\B / the dependency is pending ' / the dependency is pending q)\B `s#`a`b q)\b `s#`a`b q)b 29 q)a 29 q)\B `symbol$()
\cd – 更改目录
q)/change directory, \cd [name] q)\cd "C:\\Users\\myaccount-raj" q)\cd ../new-account q)\cd "C:\\Users\\new-account"
\d – 设置当前命名空间
q)/ sets current namespace \d [namespace] q)\d /default namespace ' q)\d .o /change to .o q.o)\d `.o q.o)\d . / return to default q)key ` /lists namespaces other than .z `q`Q`h`j`o q)\d .john /change to non-existent namespace q.john)\d `.john q.john)\d . q)\d `.
\l – 从数据库加载文件或目录
q)/ Load file or directory, \l q)\l test2.q / loading test2.q which is stored in current path. ric | date ex openP closeP MCap ----------- | ------------------------------------------------- JPMORGAN | 2008.05.23 SENSEX 18.30185 17.16319 17876 HSBC | 2002.05.21 NIFTY 2.696749 16.58846 26559 JPMORGAN | 2006.09.07 NIFTY 14.15219 20.05624 14557 HSBC | 2010.10.11 SENSEX 7.394497 25.45859 29366 JPMORGAN | 2007.10.02 SENSEX 1.558085 25.61478 20390 ric | date ex openP closeP MCap ---------- | ------------------------------------------------ INFOSYS | 2003.10.30 DOW 21.2342 7.565652 2375 RELIANCE | 2004.08.12 DOW 12.34132 17.68381 4201 SBIN | 2008.02.14 DOW 1.830857 9.006485 15465 INFOSYS | 2009.06.11 HENSENG 19.47664 12.05208 11143 SBIN | 2010.07.05 DOW 18.55637 10.54082 15873
\p – 端口号
q)/ assign port number, \p q)\p 5001i q)\p 8888 q)\p 8888i
\\ - 从 q 控制台退出
\\ - exit Exit form q.
Q 语言 - 内置函数
q编程语言有一组丰富而强大的内置函数。内置函数可以是以下类型 -
字符串函数- 将字符串作为输入并返回字符串。
聚合函数- 将列表作为输入并返回一个Atomics。
Uniform 函数- 获取一个列表并返回相同计数的列表。
数学函数- 接受数字参数并返回数字参数。
其他功能- 除上述以外的所有功能。
字符串函数
喜欢 - 模式匹配
q)/like is a dyadic, performs pattern matching, return 1b on success else 0b q)"John" like "J??n" 1b q)"John My Name" like "J*" 1b
ltrim - 删除前导空白
q)/ ltrim - monadic ltrim takes string argument, removes leading blanks q)ltrim " Rick " "Rick "
rtrim - 删除尾随空白
q)/rtrim - takes
