Go - Switch 语句
switch语句允许测试变量是否与值列表相等。每个值称为一个 case,并且针对每个switch case检查正在打开的变量。
在 Go 编程中,switch 语句有两种类型 -
表达式开关- 在表达式开关中,一个 case 包含表达式,该表达式与开关表达式的值进行比较。
类型开关- 在类型开关中,案例包含与特殊注释的开关表达式的类型进行比较的类型。
表情切换
Go 编程语言中表达式 switch语句的语法如下 -
switch(boolean-expression or integral type){
case boolean-expression or integral type :
statement(s);
case boolean-expression or integral type :
statement(s);
/* you can have any number of case statements */
default : /* Optional */
statement(s);
}
以下规则适用于switch语句 -
switch语句中使用的表达式必须具有整数或布尔表达式,或者属于类类型,其中该类具有到整数或布尔值的单个转换函数。如果未传递表达式,则默认值为 true。
一个 switch 中可以有任意数量的 case 语句。每个案例后面都跟有要比较的值和冒号。
case 的常量表达式必须与 switch 中的变量具有相同的数据类型,并且必须是常量或文字。
当打开的变量等于 case 时,将执行该 case 后面的语句。case 语句中不需要中断。
switch语句可以有一个可选的default case,它必须出现在 switch 的末尾。当所有情况都不成立时,可以使用默认情况来执行任务。默认情况下不需要中断。
流程图
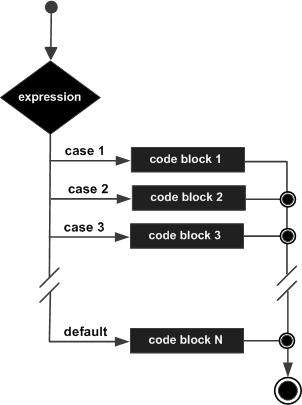
例子
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
/* local variable definition */
var grade string = "B"
var marks int = 90
switch marks {
case 90: grade = "A"
case 80: grade = "B"
case 50,60,70 : grade = "C"
default: grade = "D"
}
switch {
case grade == "A" :
fmt.Printf("Excellent!\n" )
case grade == "B", grade == "C" :
fmt.Printf("Well done\n" )
case grade == "D" :
fmt.Printf("You passed\n" )
case grade == "F":
fmt.Printf("Better try again\n" )
default:
fmt.Printf("Invalid grade\n" );
}
fmt.Printf("Your grade is %s\n", grade );
}
当上面的代码被编译并执行时,它会产生以下结果 -
Excellent! Your grade is A
类型开关
Go 编程中类型 switch语句的语法如下 -
switch x.(type){
case type:
statement(s);
case type:
statement(s);
/* you can have any number of case statements */
default: /* Optional */
statement(s);
}
以下规则适用于switch语句 -
switch语句中使用的表达式必须具有 interface{} 类型的变量。
一个 switch 中可以有任意数量的 case 语句。每个案例后面都跟有要比较的值和冒号。
case 的类型必须与 switch 中的变量的数据类型相同,并且必须是有效的数据类型。
当打开的变量等于 case 时,将执行该 case 后面的语句。case 语句中不需要中断。
switch 语句可以有一个可选的 default case,它必须出现在 switch 的末尾。当所有情况都不成立时,可以使用默认情况来执行任务。默认情况下不需要中断。
例子
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
var x interface{}
switch i := x.(type) {
case nil:
fmt.Printf("type of x :%T",i)
case int:
fmt.Printf("x is int")
case float64:
fmt.Printf("x is float64")
case func(int) float64:
fmt.Printf("x is func(int)")
case bool, string:
fmt.Printf("x is bool or string")
default:
fmt.Printf("don't know the type")
}
}
当上面的代码被编译并执行时,它会产生以下结果 -
type of x :<nil>
