
- iOS教程
- iOS - 主页
- iOS - 入门
- iOS - 环境设置
- iOS - Objective-C 基础知识
- iOS - 第一个 iPhone 应用程序
- iOS - 操作和出口
- iOS - 代表
- iOS - UI 元素
- iOS - 加速度计
- iOS - 通用应用程序
- iOS - 相机管理
- iOS - 位置处理
- iOS-SQLite 数据库
- iOS - 发送电子邮件
- iOS - 音频和视频
- iOS - 文件处理
- iOS - 访问地图
- iOS - 应用内购买
- iOS - iAd 集成
- iOS - 游戏套件
- iOS - 故事板
- iOS - 自动布局
- iOS - 推特和脸书
- iOS - 内存管理
- iOS - 应用程序调试
- iOS 有用资源
- iOS - 快速指南
- iOS - 有用的资源
- iOS - 讨论
iOS - 第一个 iPhone 应用程序
创建第一个应用程序
现在我们将创建一个简单的单视图应用程序(一个空白应用程序),它将在 iOS 模拟器上运行。
步骤如下。
步骤 1 - 打开 Xcode 并选择创建新的 Xcode 项目。

步骤 2 - 选择“单一视图应用程序”。

步骤 3 - 输入产品名称,即应用程序名称、组织名称,然后输入公司标识符。

步骤 4 - 确保选择“使用自动引用计数”,以便在超出范围时自动释放分配的资源。点击下一步。
步骤 5 - 选择项目的目录并选择创建。

步骤 6 - 您将看到如下屏幕 -

在上面的屏幕中,您将能够选择支持的方向、构建和发布设置。有一个现场部署目标,我们要支持的设备版本,让我们选择4.3,这是现在允许的最低部署目标。目前,这些都不是必需的,让我们专注于运行应用程序。
步骤 7 - 现在,在“运行”按钮附近的下拉列表中选择“iPhone 模拟器”,然后选择“运行”。

第 8 步- 就是这样;您已成功运行您的第一个应用程序。您将得到如下输出 -

现在让我们更改背景颜色,以便开始使用界面生成器。选择ViewController.xib。选择右侧的背景选项,更改颜色并运行。
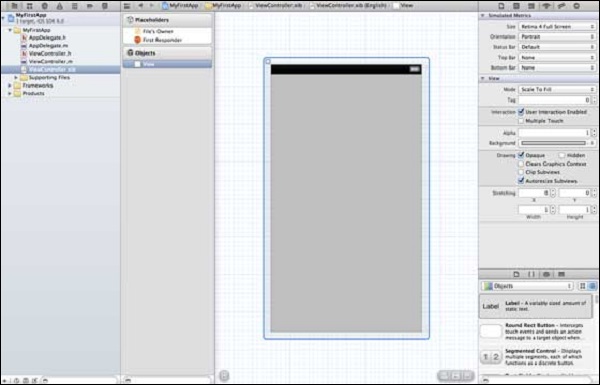
在上面的项目中,默认情况下,部署目标将设置为 iOS 6.0,并且将启用自动布局。为了确保我们的应用程序在 iOS 4.3 及以上版本的设备上运行,我们已经在创建此应用程序时修改了部署目标,但我们没有禁用自动布局。
要禁用自动布局,我们需要在每个 nib(即 xib 文件)的文件检查器中取消选择自动布局复选框。下图给出了 Xcode 项目 IDE 的各个部分(由 Apple Xcode 4 用户文档提供)。

文件检查器位于检查器选择器栏中,如上所示,并且可以在那里取消选中自动布局。当您只想定位 iOS 6 设备时,可以使用自动布局。此外,如果将部署目标提高到 iOS 6,您将能够使用许多新功能,例如存折。现在,我们坚持使用 iOS 4.3 作为部署目标。
第一个 iOS 应用程序的代码
您将发现为您的应用程序生成的五个不同文件。它们列出如下 -
- AppDelegate.h
- AppDelegate.m
- 视图控制器.h
- 视图控制器.m
- 视图控制器.xib
AppDelegate.h
// Header File that provides all UI related items. #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> // Forward declaration (Used when class will be defined /imported in future) @class ViewController; // Interface for Appdelegate @interface AppDelegate : UIResponder <UIApplicationDelegate> // Property window @property (strong, nonatomic) UIWindow *window; // Property Viewcontroller @property (strong, nonatomic) ViewController *viewController; //this marks end of interface @end
代码中的重要项目-
AppDelegate继承自处理iOS事件的UIResponder。
实现 UIApplicationDelegate 的委托方法,提供关键的应用程序事件,如完成启动、即将终止等。
UIWindow 对象来管理和协调 iOS 设备屏幕上的各种视图。它就像加载所有其他视图的基础视图。一般来说,一个应用程序只有一个窗口。
UIViewController 来处理屏幕流。
AppDelegate.m
// Imports the class Appdelegate's interface
import "AppDelegate.h"
// Imports the viewcontroller to be loaded
#import "ViewController.h"
// Class definition starts here
@implementation AppDelegate
// Method to intimate us that the application launched successfully
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
self.window = [[UIWindow alloc] initWithFrame:[[UIScreen mainScreen] bounds]];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
self.viewController = [[ViewController alloc]
initWithNibName:@"ViewController" bundle:nil];
self.window.rootViewController = self.viewController;
[self.window makeKeyAndVisible];
return YES;
}
- (void)applicationWillResignActive:(UIApplication *)application {
/* Use this method to release shared resources, save user data,
invalidate timers, and store enough application state information
to restore your application to its current state in case it is
terminated later. If your application supports background
execution, this method is called instead of
applicationWillTerminate: when the user quits.*/
}
- (void)applicationWillEnterForeground:(UIApplication *)application {
/* Called as part of the transition from the background to the
inactive state. Here you can undo many of the changes made on
entering the background.*/
}
- (void)applicationDidBecomeActive:(UIApplication *)application {
/* Restart any tasks that were paused (or not yet started) while
the application was inactive. If the application was previously in
the background, optionally refresh the user interface.*/
}
- (void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application {
/* Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if
appropriate. See also applicationDidEnterBackground:. */
}
- (void)applicationWillTerminate:(UIApplication *)application {
/* Called when the application is about to terminate. Save data if appropriate.
See also applicationDidEnterBackground:. */
}
@end
代码中的重要项目-
UIApplication 委托在这里定义。上面定义的所有方法都是 UI 应用程序委托,不包含用户定义的方法。
UIWindow对象被分配来保存应用程序分配的。
UIViewController 被分配为窗口的初始视图控制器。
为了使窗口可见,调用 makeKeyAndVisible 方法。
视图控制器.h
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h> // Interface for class ViewController @interface ViewController : UIViewController @end
代码中的重要项目-
ViewController 类继承了 UIViewController,它为 iOS 应用程序提供了基本的视图管理模型。
视图控制器.m
#import "ViewController.h"
// Category, an extension of ViewController class
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Do any additional setup after loading the view, typically from a nib.
}
- (void)didReceiveMemoryWarning {
[super didReceiveMemoryWarning];
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
@end
代码中的重要项目-
这里实现的两个方法是在基类 UIViewController 中定义的。
在视图加载后调用的 viewDidLoad 中进行初始设置。
didReceiveMemoryWarning 方法在出现内存警告时被调用。