
- Struts 2 教程
- Struts2 - 主页
- Struts2 - 基本 MVC 架构
- Struts2 - 概述
- Struts2 - 环境设置
- Struts2 - 架构
- Struts2 - 示例
- Struts2 - 配置
- Struts2 - 动作
- Struts2 - 拦截器
- Struts2 - 结果类型
- Struts2 - 价值堆栈/OGNL
- Struts2 - 文件上传
- Struts2 - 数据库访问
- Struts2 - 发送电子邮件
- Struts2 - 验证
- Struts2 - 本地化
- Struts2 - 类型转换
- Struts2 - 主题/模板
- Struts2 - 异常处理
- Struts2 - 注释
- Struts 2 集成
- Struts2-Spring
- Struts2 - 瓷砖
- Struts2-Hibernate
- Struts 2 有用资源
- Struts2 - 问题与解答
- Struts2 - 快速指南
- Struts2 - 有用的资源
- Struts2 - 讨论
Struts 2 - 动作
操作是 Struts2 框架的核心,就像任何 MVC(模型视图控制器)框架一样。每个 URL 都映射到一个特定的操作,该操作提供服务用户请求所需的处理逻辑。
但这一行动还具有另外两个重要作用。首先,操作在数据从请求到视图的传输中起着重要作用,无论是 JSP 还是其他类型的结果。其次,该操作必须协助框架确定哪个结果应该呈现将在请求响应中返回的视图。
创建动作
Struts2中操作的唯一要求是必须有一个无参方法返回 String 或 Result 对象,并且必须是 POJO。如果未指定无参数方法,则默认Behave是使用execute() 方法。
您可以选择扩展ActionSupport类,它实现了六个接口,包括Action接口。操作界面如下 -
public interface Action {
public static final String SUCCESS = "success";
public static final String NONE = "none";
public static final String ERROR = "error";
public static final String INPUT = "input";
public static final String LOGIN = "login";
public String execute() throws Exception;
}
让我们看一下 Hello World 示例中的操作方法 -
package com.tutorialspoint.struts2;
public class HelloWorldAction {
private String name;
public String execute() throws Exception {
return "success";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
为了说明操作方法控制视图的点,让我们对执行方法进行以下更改并扩展 ActionSupport 类,如下所示 -
package com.tutorialspoint.struts2;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class HelloWorldAction extends ActionSupport {
private String name;
public String execute() throws Exception {
if ("SECRET".equals(name)) {
return SUCCESS;
} else {
return ERROR;
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
在此示例中,我们在执行方法中有一些逻辑来查看 name 属性。如果属性等于字符串“SECRET”,则返回SUCCESS作为结果,否则返回ERROR作为结果。因为我们扩展了ActionSupport,所以我们可以使用字符串常量SUCCESS和ERROR。现在,让我们修改 struts.xml 文件如下 -
<?xml version = "1.0" Encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<constant name = "struts.devMode" value = "true" />
<package name = "helloworld" extends = "struts-default">
<action name = "hello"
class = "com.tutorialspoint.struts2.HelloWorldAction"
method = "execute">
<result name = "success">/HelloWorld.jsp</result>
<result name = "error">/AccessDenied.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
创建视图
让我们在 Eclipse 项目的 WebContent 文件夹中创建以下 jsp 文件HelloWorld.jsp。为此,请右键单击项目资源管理器中的 WebContent 文件夹,然后选择“新建”>“JSP 文件”。如果返回结果为 SUCCESS,则将调用此文件,SUCCESS 是 Action 接口中定义的字符串常量“success” -
<%@ page contentType = "text/html; charset = UTF-8" %>
<%@ taglib prefix = "s" uri = "/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello World, <s:property value = "name"/>
</body>
</html>
以下是在操作结果为 ERROR(等于字符串常量“error”)时框架将调用的文件。以下是AccessDenied.jsp的内容
<%@ page contentType = "text/html; charset = UTF-8" %>
<%@ taglib prefix = "s" uri = "/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Access Denied</title>
</head>
<body>
You are not authorized to view this page.
</body>
</html>
我们还需要在 WebContent 文件夹中创建index.jsp 。该文件将用作初始操作 URL,用户可以单击该 URL 来告诉 Struts 2 框架调用HelloWorldAction 类的执行方法并呈现 HelloWorld.jsp 视图。
<%@ page language = "java" contentType = "text/html; charset = ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding = "ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix = "s" uri = "/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World From Struts2</h1>
<form action = "hello">
<label for = "name">Please enter your name</label><br/>
<input type = "text" name = "name"/>
<input type = "submit" value = "Say Hello"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
就是这样,web.xml 文件不需要更改,所以让我们使用我们在示例章节中创建的相同 web.xml。现在,我们已准备好使用 Struts 2 框架运行Hello World应用程序。
执行应用程序
右键单击项目名称,然后单击“导出”>“WAR文件”以创建 War 文件。然后将此 WAR 部署到 Tomcat 的 webapps 目录中。最后,启动 Tomcat 服务器并尝试访问 URL http://localhost:8080/HelloWorldStruts2/index.jsp。这将为您提供以下屏幕 -
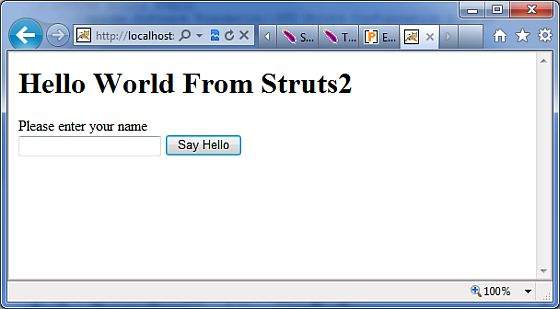
让我们输入一个单词“秘密”,您应该看到以下页面 -

现在输入“秘密”以外的任何单词,您应该看到以下页面 -

创建多个动作
您将经常定义多个操作来处理不同的请求并向用户提供不同的 URL,因此您将定义不同的类,如下所示 -
package com.tutorialspoint.struts2;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
class MyAction extends ActionSupport {
public static String GOOD = SUCCESS;
public static String BAD = ERROR;
}
public class HelloWorld extends ActionSupport {
...
public String execute() {
if ("SECRET".equals(name)) return MyAction.GOOD;
return MyAction.BAD;
}
...
}
public class SomeOtherClass extends ActionSupport {
...
public String execute() {
return MyAction.GOOD;
}
...
}
您将在 struts.xml 文件中配置这些操作,如下所示 -
<?xml version = "1.0" Encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<constant name = "struts.devMode" value = "true" />
<package name = "helloworld" extends = "struts-default">
<action name = "hello"
class = "com.tutorialspoint.struts2.HelloWorld"
method = "execute">
<result name = "success">/HelloWorld.jsp</result>
<result name = "error">/AccessDenied.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name = "something"
class = "com.tutorialspoint.struts2.SomeOtherClass"
method = "execute">
<result name = "success">/Something.jsp</result>
<result name = "error">/AccessDenied.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
正如您在上面的假设示例中看到的,操作结果SUCCESS和ERROR是重复的。
为了解决这个问题,建议您创建一个包含结果的类。