
- Xamarin 教程
- Xamarin - 主页
- Xamarin - 安装
- Xamarin - 首次应用
- Xamarin - 应用程序清单
- Xamarin - Android 资源
- Xamarin - Android 活动生命周期
- Xamarin - 权限
- Xamarin - 构建应用程序 GUI
- Xamarin - 菜单
- Xamarin - 布局
- Xamarin - Android 小部件
- Xamarin - Android 对话框
- Xamarin - 画廊
- Xamarin - Andriod 视图
- Xamarin - 多屏应用程序
- Xamarin - 部署您的应用程序
- Xamarin 有用资源
- Xamarin - 快速指南
- Xamarin - 有用的资源
- Xamarin - 讨论
Xamarin - 快速指南
Xamarin - 安装
Xamarin 构建于 .NET Framework 之上。它允许人们创建可以轻松跨多个平台运行的应用程序。在本教程中,我们将解释如何使用 Xamarin 交付本机 iOS、Android 和 Windows 应用程序。
我们首先讨论如何在 Windows 和 Mac 系统中安装 Xamarin。
系统要求
Windows
具有至少 2GB RAM 并运行 Windows 7 或更高版本的计算机(强烈建议使用 Windows 8-10)
Visual Studio 2012 专业版或更高版本
用于 Visual Studio 的 Xamarin
苹果
- 运行 OS X Yosemite (10.10) 或更高版本的 Mac 计算机
- Xamarin iOS SDK
- Apple 的 Xcode (7+) IDE 和 iOS SDK
- Xamarin工作室
在 Windows 上安装
从https://www.xamarin.com/download下载 Xamarin 安装程序在运行 Xamarin 安装程序之前,请确保您已在计算机上安装 Android SDK 和 Java SDK。
运行下载的安装程序以开始安装过程 -
将出现 Xamarin 许可协议屏幕。单击“下一步”按钮接受协议。
安装程序将搜索任何缺少的组件并提示您下载并安装它们。
Xamarin安装完成后,单击“关闭”按钮退出并准备开始使用Xamarin。
在 Mac 上安装
在 Mac 系统上下载 Xamarin Studio 安装程序。
运行您下载的 Xamarin 安装程序并按照安装向导中给出的步骤进行操作。
安装完成后,您可以开始在系统上使用 Xamarin。
Xamarin - 首次应用
在本章中,我们将了解如何使用 Xamarin 创建小型 Android 应用程序。
你好,Xamarin!应用
首先,启动 Visual Studio 的新实例并转到File → New → Project。
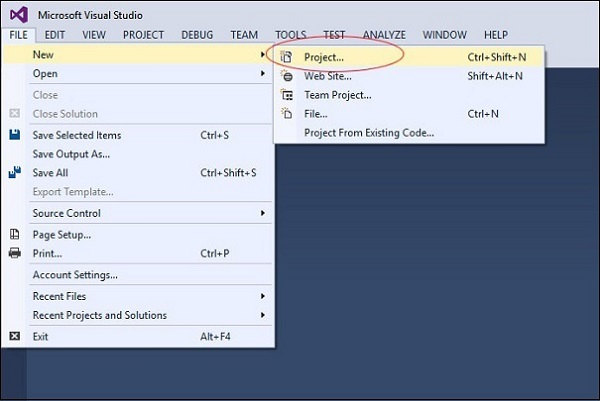
在出现的菜单对话框中,转到Templates → Visual C# → Android → Blank App (Android)。
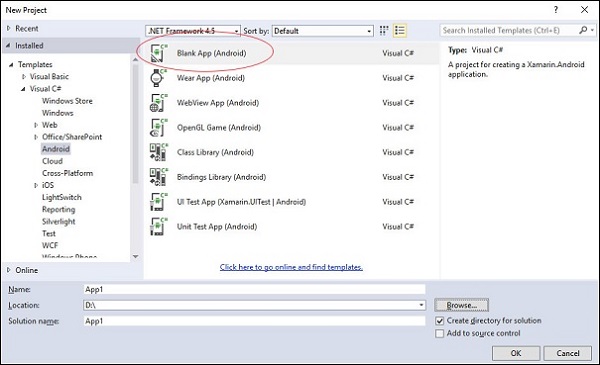
为您的应用程序指定一个合适的名称。在我们的例子中,我们将其命名为“helloWorld”并将其保存在提供的默认位置。接下来,单击“确定”按钮加载新的“helloXamarin”项目。
在解决方案上,打开资源 → 布局 → Main.axml文件。从设计视图切换到源文件,然后键入以下代码行来构建您的应用程序。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<TextView
android:text = "@string/HelloXamarin"
android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/textView2"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</LinearLayout>
在上面的代码中,我们创建了一个新的 Android textview。接下来,打开文件夹值并双击Strings.xml将其打开。在这里,我们将存储有关上面创建的按钮的信息和值。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?> <resources> <string name = "HelloXamarin">Hello World, I am Xamarin!</string> <string name = "ApplicationName">helloWorld</string> </resources>
打开MainActivity.cs文件并将现有代码替换为以下代码行。
using System;
using Android.App;
using Android.Content;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Widget;
using Android.OS;
namespace HelloXamarin {
public class MainActivity : Activity {
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle) {
base.OnCreate(bundle);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
}
}
}
保存应用程序。构建并运行它以在 Android 模拟器中显示创建的应用程序。
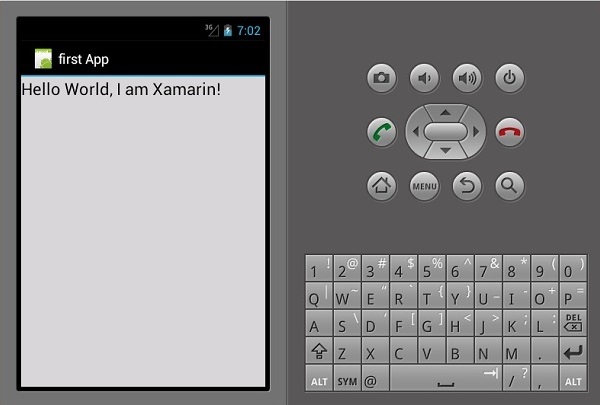
如果您没有 Android 模拟器,请按照下一节中给出的步骤创建一个。
设置 Android 模拟器
在 Visual Studio 菜单上,转到Tools → Android → Android Emulator Manager。在出现的弹出窗口中,单击“创建”按钮。它将显示以下屏幕。
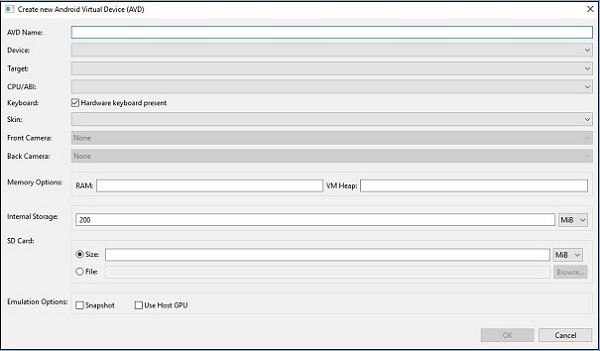
在上面的屏幕上,提供您想要的AVD 名称。选择适合您显示器的设备,例如 Nexus 4 英寸显示器。选择您的目标平台。始终建议在最低目标平台上进行测试,例如 API 10 Android 2.3 (Gingerbread),以确保您的应用程序可以在所有 Android 平台上运行。
填写其余字段并单击“确定”按钮。您的模拟器现已准备就绪。您可以从现有 Android 虚拟设备列表中选择它,然后单击“开始”启动它。
修改HelloXamarin应用程序
在本节中,我们将修改我们的项目并创建一个按钮,单击该按钮将显示文本。打开main.axml并切换到源代码视图。创建文本视图后,我们将添加一个按钮,如下所示。
<Button android:id = "@+id/MyButton" android:layout_width = "fill_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:text = "@string/ButtonClick" />
添加按钮后,我们的完整代码将如下所示 -
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<TextView
android:text = "@string/HelloXamarin"
android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/textView2" />
<Button
android:id = "@+id/MyButton"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "@string/ButtonClick" />
</LinearLayout>
接下来,我们在strings.xml文件中注册按钮值。
<string name = "ButtonClick">Click Me!</string>
在strings.xml文件中添加按钮后,我们将打开MainActivity.cs文件,为按钮添加单击时的操作,如以下代码所示。
using System;
using Android.App;
using Android.Content;
using Android.Runtime;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Widget;
using Android.OS;
namespace HelloXamarin {
[Activity(Label = "HelloXamarin", MainLauncher = true, Icon = "@drawable/icon")]
public class MainActivity : Activity {
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle) {
base.OnCreate(bundle);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
Button button = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.MyButton);
button.Click += delegate { button.Text = "Hello world I am your first App"; };
}
}
}
接下来,构建并运行您的应用程序。
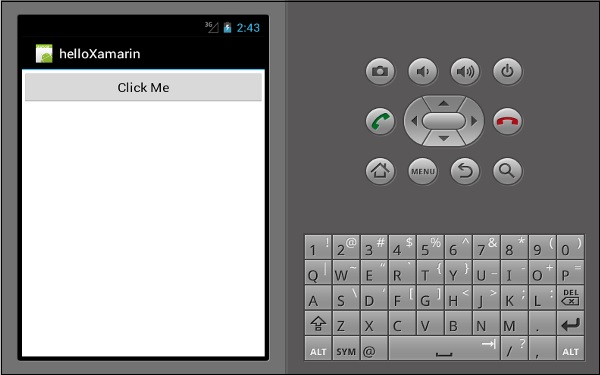
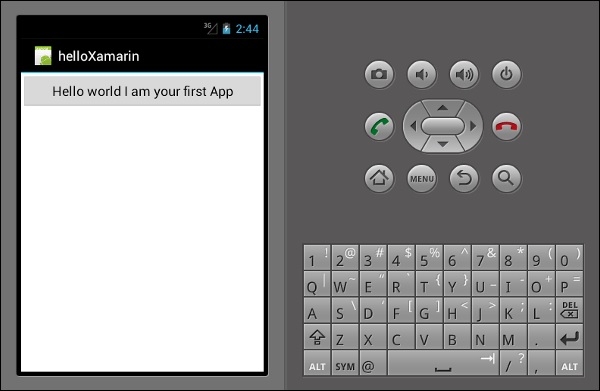
单击按钮后,您将得到以下输出 -
Xamarin - 应用程序清单
所有 Android 应用程序都有一个清单文件,通常称为AndroidManifest.xml。清单文件包含应用程序成功运行所需的有关 Android 平台的所有信息。
在这里,我们列出了清单文件的一些重要功能 -
它声明了应用程序所需的最低 API 级别。
它声明应用程序所需的权限,例如相机、位置等。
它授予应用程序使用或所需的硬件和软件功能的权限。
它列出了应用程序必须链接的库。
以下屏幕截图显示了清单文件。
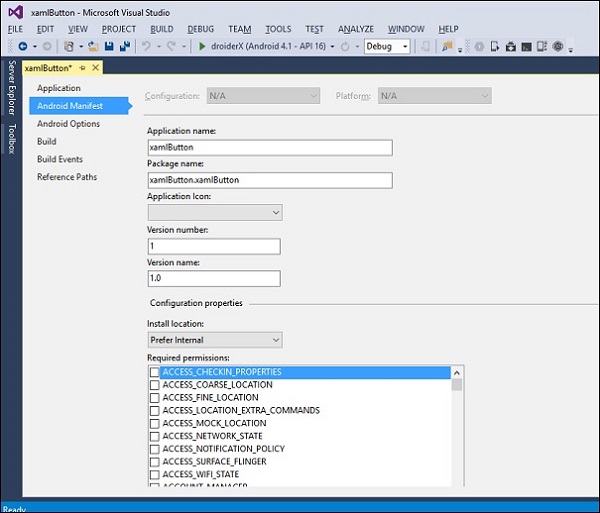
应用程序名称- 它指的是您的应用程序的标题
包名称- 这是用于识别您的应用程序的唯一名称。
应用程序图标- 它是显示在 Android 主屏幕上的应用程序图标。
版本号- 这是一个单一的数字,用于显示您的应用程序的一个版本比另一个版本更新。
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:versionCode="1" >
版本名称- 这是您的应用程序的用户友好版本字符串,用户将在您的应用程序设置和 Google PlayStore 上看到。以下代码显示了版本名称的示例。
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:versionName="1.0.0">
最低 Android 版本- 这是您的应用程序支持的最低 Android 版本平台。
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="16" />
在上面的示例中,我们的最低 Android 版本是 API Level 16,通常称为JELLY BEAN。
目标 Android 版本- 这是您的应用程序编译所针对的 Android 版本。
Xamarin - Android 资源
创建新的 Android 项目时,默认情况下会添加一些文件到该项目中。我们将这些默认项目文件和文件夹称为Android 资源。看看下面的截图。
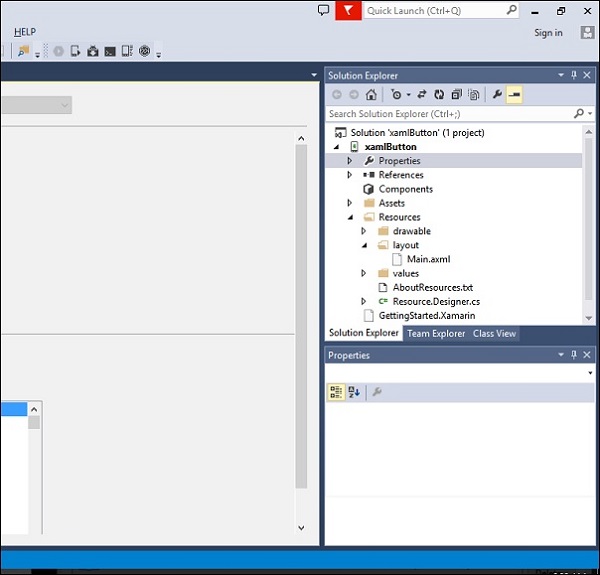
默认的 Android 资源包括以下内容 -
AndroidManifest.xml 文件- 它包含有关 Android 应用程序的信息,例如应用程序名称、权限等。
资源文件夹- 资源可以是图像、布局、字符串等,可以通过 Android 的资源系统加载。
Resources/drawable 文件夹- 它存储您将在应用程序中使用的所有图像。
Resources/layout 文件夹- 它包含 Android 用于构建用户界面的所有 Android XML 文件 (.axml)。
资源/值文件夹- 它包含 XML 文件,用于在整个应用程序中声明字符串(和其他类型)的键值对。这就是 Android 上通常设置多种语言本地化的方式。
Resources.designer.cs - 该文件是在创建 Android 投影时自动创建的,它包含引用 Android 资源的唯一标识符。
MainActivity.cs 文件- 这是 Android 应用程序的第一个 Activity,也是主应用程序操作启动的地方。
可以通过存储在resources.designer.cs文件中的唯一 ID以编程方式访问资源文件。该 ID 包含在名为Resource 的类下。添加到项目中的任何资源都会在资源类中自动生成。
以下代码显示了如何创建包含七个图像的 gridview 项目 -
namespace HelloGridView {
[System.CodeDom.Compiler.GeneratedCodeAttribute
("Xamarin.Android.Build.Tas ks",
"1.0.0.0")]
public partial class Resource {
static Resource() {
global::Android.Runtime.ResourceIdManager.UpdateIdValues();
}
public static void UpdateIdValues() {}
public partial class Attribute {
static Attribute() {
global::Android.Runtime.ResourceIdManager.UpdateIdValues();
}
private Attribute() {}
}
public partial class Drawable {
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020000
public const int Icon = 2130837504;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020001
public const int img1 = 2130837505;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020002
public const int img2 = 2130837506;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020003
public const int img3 = 2130837507;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020004
public const int img4 = 2130837508;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020005
public const int img5 = 2130837509;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020006
public const int img6 = 2130837510;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f020007
public const int img7 = 2130837511;
static Drawable() {
global::Android.Runtime.ResourceIdManager.UpdateIdValues();
}
private Drawable() {}
}
public partial class Id {
// aapt resource value: 0x7f050000
public const int gridview = 2131034112;
static Id() {
global::Android.Runtime.ResourceIdManager.UpdateIdValues();
}
private Id() {}
}
public partial class Layout {
// aapt resource value: 0x7f030000
public const int Main = 2130903040;
static Layout() {
global::Android.Runtime.ResourceIdManager.UpdateIdValues();
}
private Layout() {}
}
public partial class String {
// aapt resource value: 0x7f040001
public const int ApplicationName = 2130968577;
// aapt resource value: 0x7f040000
public const int Hello = 2130968576;
static String() {
global::Android.Runtime.ResourceIdManager.UpdateIdValues();
}
private String() {}
}
}
}
从上面的代码中,七个图像在名为drawable的类中引用。这些图像是以编程方式添加的。如果用户将另一个图像添加到项目中,它也将被添加到可绘制类中。项目中包含的gridview也被添加并存储在自己的类中。资源文件夹中包含的每个项目都会自动生成并存储在一个类中。
Xamarin - Android 活动生命周期
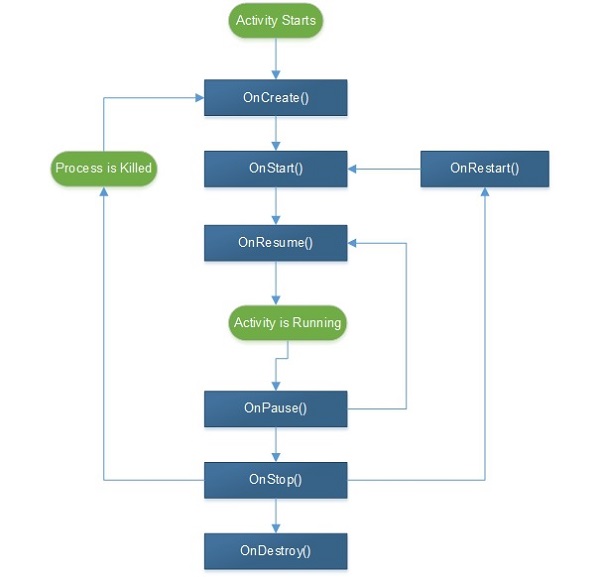
当用户浏览 Android 应用程序时,会发生一系列事件。例如,当用户启动应用程序(例如 Facebook 应用程序)时,它会启动并在前台对用户可见,onCreate() → onStart() → onResume()。
如果另一个活动开始,例如,有电话打进来,那么 Facebook 应用程序将转到后台,而电话则转到前台。我们现在有两个进程正在运行。
onPause() --- > onStop()
电话结束后,Facebook 应用程序返回前台。调用了三个方法。
onRestart() --- > onStart() --- > onResume()
Android Activity 有 7 个生命周期过程。它们包括 -
onCreate - 首次创建活动时调用。
onStart - 当活动启动并对用户可见时调用。
onResume - 当活动开始与用户交互时调用。用户输入发生在这个阶段。
onPause - 当活动在后台运行但尚未被终止时调用。
onStop - 当活动不再对用户可见时调用。
onRestart - 在活动停止后再次开始之前调用。当用户返回到先前已停止的活动时,通常会调用它。
onDestroy - 这是从内存中删除活动之前的最后一次调用。
下图显示了 Android 活动生命周期 -
Xamarin - 权限
在 Android 中,默认情况下,任何应用程序都无权执行任何可能对用户或操作系统产生影响的操作。为了让应用程序执行任务,它必须声明权限。在获得Android系统的许可之前,应用程序无法执行该任务。这种权限机制可以阻止应用程序在未经用户同意的情况下按照自己的意愿行事。
权限将记录在AndroidManifest.xml文件中。要添加权限,我们双击属性,然后转到 Android Man所需的权限将会出现。检查您要添加的适当权限。
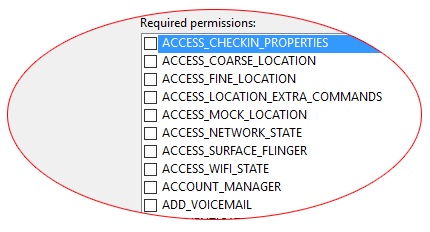
相机- 它提供访问设备相机的权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
互联网- 它提供对网络资源的访问。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
ReadContacts - 它提供读取设备上的联系人的访问权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_CONTACTS" />
ReadExternalStorage - 它提供在外部存储上读取和存储数据的访问。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
日历- 它允许应用程序访问用户设备上的日历和事件。此权限可能很危险,因为它授予应用程序在所有者不知情的情况下向客人发送电子邮件的能力。添加此权限的语法如下所示 -
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission-group.CALENADAR" />
SMS - 具有此权限的应用程序能够使用设备的消息服务。它包括阅读、编写和编辑短信和彩信。其语法如下所示。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission-group.SMS" />
位置- 具有此权限的应用程序可以使用 GPS 网络访问设备的位置。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission-group.LOCATION" />
蓝牙- 具有此权限的应用程序可以与其他支持蓝牙的设备无线交换数据文件。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
Xamarin - 构建应用程序 GUI
文本视图
TextView 是 Android 小部件中非常重要的组件。它主要用于在 Android 屏幕上显示文本。
要创建文本视图,只需打开main.axml并在线性布局标记之间添加以下代码。
<TextView android:text = "Hello I am a text View" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:id = "@+id/textview1" />
按钮
按钮是用于在单击时触发事件的控件。在Main.axml文件下,键入以下代码以创建按钮。
<Button android:id = "@+id/MyButton" android:layout_width = "fill_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:text = "@string/Hello" />
打开Resources\Values\Strings.xml并在 <resources> 标记之间键入以下代码行。
<string name="Hello">Click Me!</string>
上面的代码提供了我们创建的按钮的值。接下来,我们打开MainActivity.cs并创建单击按钮时要执行的操作。在base.OnCreate (bundle) 方法下键入以下代码。
Button button = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.MyButton);
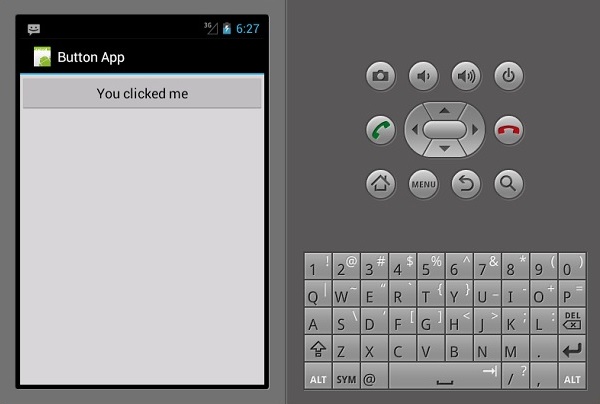
button.Click += delegate { button.Text = "You clicked me"; };
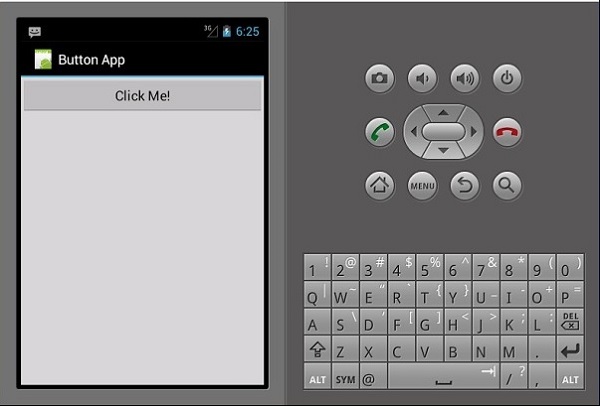
当用户单击按钮时,上面的代码显示“You Clicked Me”。
FindViewById<< -->此方法查找已识别视图的 ID。它在 .axml 布局文件中搜索 id。
复选框
当想要从一组选项中选择多个选项时,可以使用复选框。在此示例中,我们将创建一个复选框,选中该复选框后,会显示一条消息,表明已选中该复选框,否则显示未选中状态。
首先,我们在项目中打开Main.axml文件,然后键入以下代码行来创建一个复选框。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<CheckBox
android:text = "CheckBox"
android:padding = "25dp"
android:layout_width = "300dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/checkBox1"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_blue_dark" />
</LinearLayout>
接下来,转到MainActivity.cs添加功能代码。
CheckBox checkMe = FindViewById<CheckBox>(Resource.Id.checkBox1);
checkMe.CheckedChange += (object sender, CompoundButton.CheckedChangeEventArgs e) => {
CheckBox check = (CheckBox)sender;
if(check.Checked) {
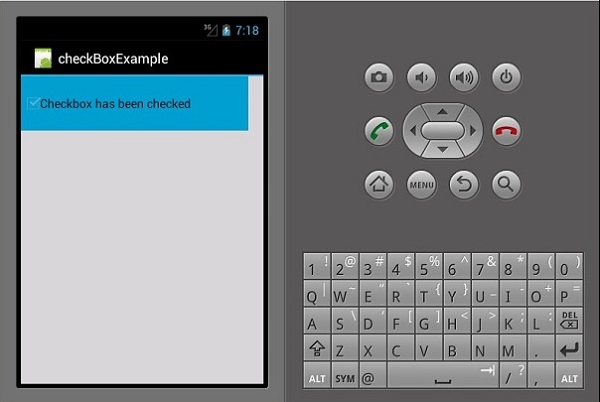
check.Text = "Checkbox has been checked";
} else {
check.Text = "Checkbox has not been checked";
}
};
从上面的代码中,我们首先使用findViewById找到复选框。接下来,我们为复选框创建一个处理程序方法,并在处理程序中创建一个 if else 语句,该语句根据所选结果显示一条消息。
CompoundButton.CheckedChangeEventArgs → 当复选框状态更改时,此方法会触发事件。
进度条
进度条是用于显示操作进度的控件。要添加进度条,请在Main.axml文件中添加以下代码行。
<ProgressBar style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:id = "@+id/progressBar1" />
接下来,转到MainActivity.cs并设置进度条的值。
ProgressBar pb = FindViewById<ProgressBar>(Resource.Id.progressBar1); pb.Progress = 35;
在上面的代码中,我们创建了一个值为 35 的进度条。
单选按钮
这是一个 Android 小部件,允许人们从一组选项中选择一个。在本节中,我们将创建一个包含汽车列表的单选组,该列表将检索选中的单选按钮。
首先,我们添加一个单选按钮组和一个文本视图,如以下代码所示 -
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "@android:color/darker_gray"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<TextView
android:text = "What is your favourite Car"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/textView1"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/radioGroup1"
android:backgroundTint = "#a52a2aff"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark">
<RadioButton
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Ferrari"
android:id = "@+id/radioFerrari" />
<RadioButton
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Mercedes"
android:id = "@+id/radioMercedes" />
<RadioButton
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Lamborghini"
android:id = "@+id/radioLamborghini" />
<RadioButton
android:text = "Audi"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/radioAudi" />
</RadioGroup>
</LinearLayout>
为了执行操作,当单击单选按钮时,我们添加一个活动。转到MainActivity.cs并创建一个新的事件处理程序,如下所示。
private void onClickRadioButton(object sender, EventArgs e) {
RadioButton cars = (RadioButton)sender;
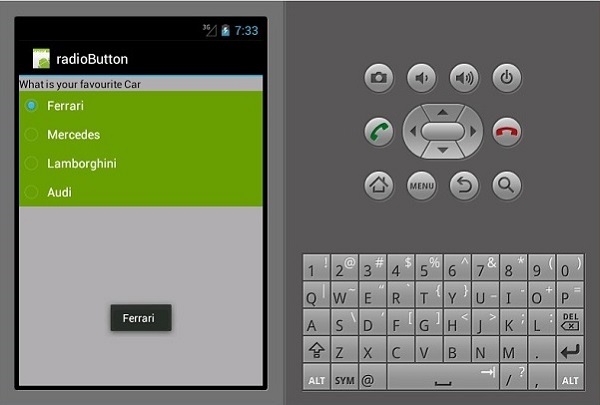
Toast.MakeText(this, cars.Text, ToastLength.Short).Show
();
}
Toast.MakeText() →这是一个视图方法,用于在小弹出窗口中显示消息/输出。在OnCreate()方法底部SetContentView()之后,添加以下代码段。这将捕获每个单选按钮并将它们添加到我们创建的事件处理程序中。
RadioButton radio_Ferrari = FindViewById<RadioButton> (Resource.Id.radioFerrari); RadioButton radio_Mercedes = FindViewById<RadioButton> (Resource.Id.radioMercedes); RadioButton radio_Lambo = FindViewById<RadioButton> (Resource.Id.radioLamborghini); RadioButton radio_Audi = FindViewById<RadioButton> (Resource.Id.radioAudi); radio_Ferrari.Click += onClickRadioButton; radio_Mercedes.Click += onClickRadioButton; radio_Lambo.Click += onClickRadioButton; radio_Audi.Click += onClickRadioButton;
现在,运行您的应用程序。它应该显示以下屏幕作为输出 -
切换按钮
切换按钮用于在两种状态之间切换,例如,它可以在ON和OFF之间切换。打开Resources\layout\Main.axml并添加以下代码行以创建切换按钮。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<ToggleButton
android:id = "@+id/togglebutton"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textOn = "Torch ON"
android:textOff = "Torch OFF"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</LinearLayout>
我们可以在单击切换栏时向其添加操作。打开MainActivity.cs并在OnCreate()方法类后面添加以下代码行。
ToggleButton togglebutton = FindViewById<ToggleButton> (Resource.Id.togglebutton);
togglebutton.Click += (o, e) => {
if (togglebutton.Checked)
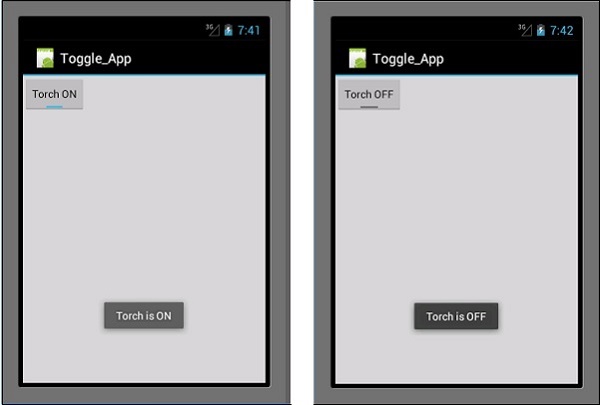
Toast.MakeText(this, "Torch is ON", ToastLength.Short).Show ();
else
Toast.MakeText(this, "Torch is OFF",
ToastLength.Short).Show();
};
现在,当您运行应用程序时,它应该显示以下输出 -
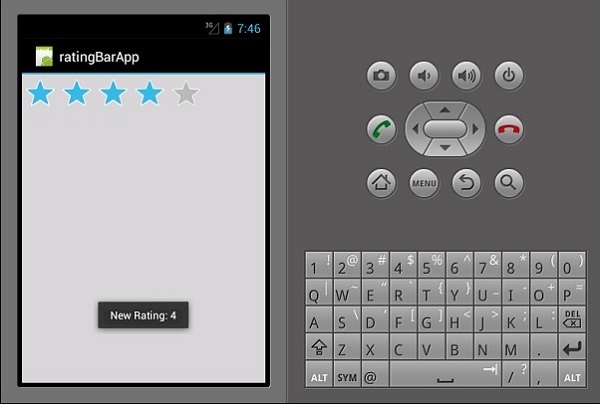
收视率栏
评级栏是一个由星星组成的表单元素,应用程序用户可以使用它来评价您为他们提供的内容。在Main.axml文件中,创建一个新的 5 星评级栏。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<RatingBar
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/ratingBar1"
android:numStars = "5"
android:stepSize = "1.0" />
</LinearLayout>
运行应用程序时,它应该显示以下输出 -
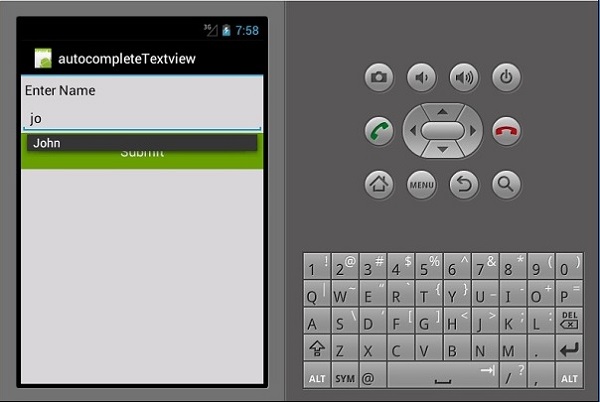
自动完成文本视图
这是一个文本视图,在用户打字时显示完整的建议。我们将创建一个自动完成文本视图,其中包含人员姓名列表和一个按钮,单击该按钮将向我们显示所选的姓名。
打开Main.axml并编写以下代码。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<TextView
android:text = "Enter Name"
android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/textView1"
android:padding = "5dp"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<AutoCompleteTextView
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/autoComplete1"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<Button
android:text = "Submit"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/btn_Submit"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</LinearLayout>
上面的代码生成一个用于输入的 TextView、用于显示建议的AutoCompleteTextView以及一个用于显示从 TextView 输入的名称的按钮。转到MainActivity.cs添加功能。
创建一个新的事件处理程序方法,如下所示。
protected void ClickedBtnSubmit(object sender, System.EventArgs e){
if (autoComplete1.Text != ""){
Toast.MakeText(this, "The Name Entered ="
+ autoComplete1.Text, ToastLength.Short).Show();
} else {
Toast.MakeText(this, "Enter a Name!", ToastLength.Short).Show();
}
}
创建的处理程序检查自动完成文本视图是否为空。如果不为空,则显示所选的自动完成文本。在OnCreate()类中键入以下代码。
autoComplete1 = FindViewById<AutoCompleteTextView>(Resource.Id.autoComplete1);
btn_Submit = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btn_Submit);
var names = new string[] { "John", "Peter", "Jane", "Britney" };
ArrayAdapter adapter = new ArrayAdapter<string>(this,
Android.Resource.Layout.SimpleSpinnerItem, names);
autoComplete1.Adapter = adapter;
btn_Submit.Click += ClickedBtnSubmit;
ArrayAdapter - 这是一个集合处理程序,它从列表集合中读取数据项并将它们作为视图返回或在屏幕上显示它们。
现在,当您运行该应用程序时,它应该显示以下输出。
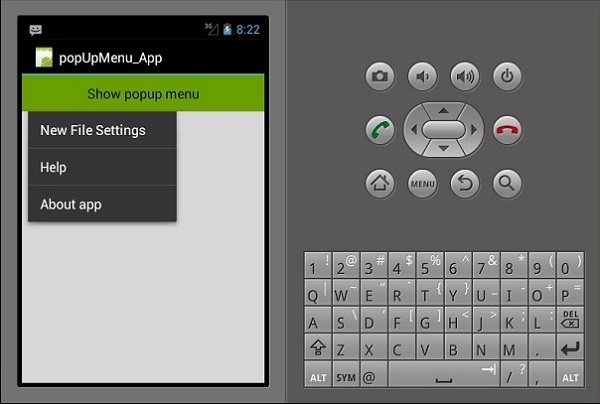
Xamarin - 菜单
弹出菜单
弹出菜单是指附加到视图的菜单;它也称为快捷菜单。让我们看看如何向 Android 应用程序添加弹出菜单。
创建一个新项目并将其命名为popUpMenu App。打开Main.axml并创建一个用于显示弹出菜单的按钮。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<Button
android:id = "@+id/popupButton"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Show popup menu"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</LinearLayout>
在Resources文件夹下创建一个新文件夹并将其命名为Menu。在 Menu 文件夹中,添加一个名为popMenu.xml的新 xml 文件。
在popMenu.xml下,添加以下菜单项。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:id = "@+id/file_settings"
android:icon = "@drawable/img_settings"
android:title = "Settings"
android:showAsAction = "ifRoom">
<item
android:id = "@+id/new_game1"
android:icon = "@drawable/imgNew"
android:title = "New File Settings"/>
<item
android:id = "@+id/help"
android:icon = "@drawable/img_help"
android:title = "Help" />
<item
android:id = "@+id/about_app"
android:icon = "@drawable/img_help"
android:title = "About app"/>
</item>
</menu>
添加菜单项后,转到mainActivity.cs以在单击按钮时显示弹出菜单。
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle) {
base.OnCreate(bundle);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
Button showPopupMenu = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.popupButton);
showPopupMenu.Click += (s, arg) => {
PopupMenu menu = new PopupMenu(this, showPopupMenu);
menu.Inflate(Resource.Menu.popMenu);
menu.Show();
};
}
现在,构建并运行您的应用程序。它应该产生以下输出 -
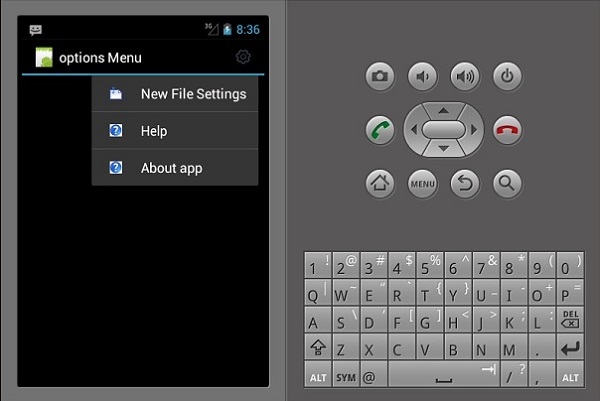
选项菜单
选项菜单是一个App的主要菜单的集合,主要用于存储设置、搜索等。这里,我们要创建一个设置菜单,里面有三个项目,即新建文件设置、帮助和关于应用程序。
要创建选项菜单,我们必须在资源文件夹中创建一个新的 XML 布局文件。首先,我们将添加一个新的 XML 文件。右键单击Layout 文件夹,然后转到“添加”→“新建项目”→“Visual C#”→“XML 文件”。
为布局文件选择合适的名称。在我们的示例中,我们将调用我们的文件myMenu.xml。
在myMenu.xml中,我们将创建一个新菜单并在其中添加项目。以下代码演示了如何执行此操作。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:id = "@+id/file_settings"
android:icon = "@drawable/img_settings"
android:title = "Settings"
android:showAsAction = "ifRoom">
<menu>
<item
android:id = "@+id/new_game1"
android:icon = "@drawable/imgNew"
android:title = "New File Settings" />
<item
android:id = "@+id/help"
android:icon = "@drawable/img_help"
android:title = "Help" />
<item
android:id = "@+id/about_app"
android:icon = "@drawable/img_help"
android:title = "About app"/>
</menu>
</item>
</menu>
接下来,我们导航到MainActivity.cs并为onOptionsMenu()创建一个重写类。
public override bool OnCreateOptionsMenu(IMenu menu) {
MenuInflater.Inflate(Resource.Menu.myMenu, menu);
return base.OnPrepareOptionsMenu(menu);
}
接下来,我们创建一个操作来响应选择的设置菜单。为此,我们为OnOptionsItemSelected()菜单创建另一个覆盖类。
public override bool OnOptionsItemSelected(IMenuItem item) {
if (item.ItemId == Resource.Id.file_settings) {
// do something here...
return true;
}
return base.OnOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
我们最终的完整代码如下所示 -
namespace optionsMenuApp {
[Activity(Label = "options Menu", MainLauncher = true, Icon = "@drawable/icon")]
public class MainActivity : Activity {
public override bool OnCreateOptionsMenu(IMenu menu) {
MenuInflater.Inflate(Resource.Menu.myMenu, menu);
return base.OnPrepareOptionsMenu(menu);
}
public override bool OnOptionsItemSelected(IMenuItem item) {
if (item.ItemId == Resource.Id.file_settings) {
// do something here...
return true;
}
return base.OnOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
}
现在,构建并运行您的应用程序。它应该产生以下输出 -
Xamarin - 布局
线性布局
在线性布局中,内容以水平或垂直方式排列。
线性布局 ─ 水平
该布局的内容是水平排列的。对于此演示,我们将创建 3 个按钮并以线性布局水平排列它们。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "horizontal"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:minWidth="25px"
android:minHeight="25px">
<Button
android:id="@+id/MyButton1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 1"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/MyButton2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 2"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/MyButton3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</LinearLayout>
结果输出如下所示 -
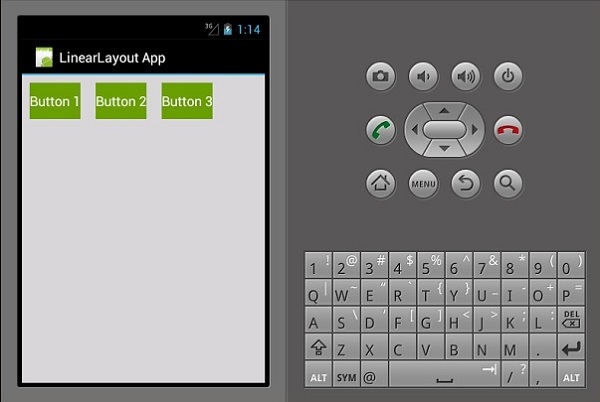
线性布局 ─ 垂直
这种类型的布局以垂直方式放置子视图。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:minWidth = "25px"
android:minHeight = "25px">
<Button
android:id = "@+id/MyButton1"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_margin = "10dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Button 1"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
<Button
android:id = "@+id/MyButton2"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_margin = "10dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Button 2"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
<Button
android:id = "@+id/MyButton3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_margin = "10dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text="Button 3"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</LinearLayout>
其结果输出如下 -
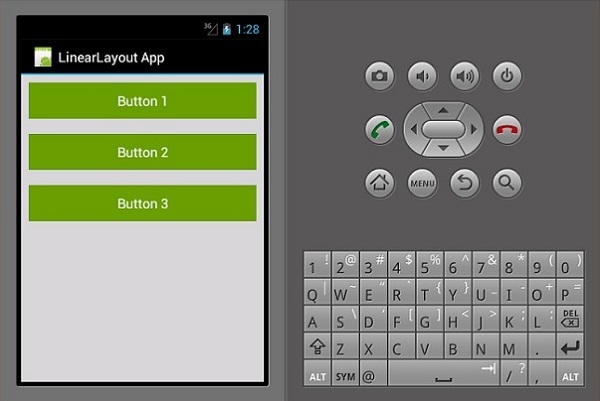
相对布局
在此视图中,子视图的位置是相对于其父视图或其兄弟视图的。在下面的示例中,我们将创建 3 个 EditText 视图和一个按钮,然后将它们相对对齐。
创建一个新项目并将其命名为相对布局应用程序。打开main.axml并添加以下代码。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent"
android:paddingLeft = "16dp"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:paddingRight = "16dp">
<EditText
android:id = "@+id/name"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:hint = "First Name"
android:textColorHint = "@android:color/background_dark"
android:textColor = "@android:color/background_dark" />
<EditText
android:id = "@+id/lastName"
android:layout_width = "0dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:hint = "Last Name"
android:layout_below = "@id/name"
android:textColorHint = "@android:color/background_dark"
android:textColor = "@android:color/background_dark"
android:layout_alignParentLeft = "true"
android:layout_toLeftOf = "@+id/age" />
<EditText
android:id = "@id/age"
android:layout_width = "80dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_below = "@id/name"
android:hint = "Age"
android:textColorHint = "@android:color/background_dark"
android:textColor = "@android:color/background_dark"
android:layout_alignParentRight = "true" />
<Button
android:layout_width = "85dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_below = "@id/age"
android:layout_alignParentRight = "true"
android:text = "Submit"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</RelativeLayout>
我们在此代码中使用的重要参数是 -
android:layout_below - 它将子视图元素对齐到其父视图元素下方。
android:layout_alignParentLeft - 将父元素向左对齐。
android:layout_toLeftOf - 此属性将一个元素与另一个元素的左侧对齐。
android:layout_alignParentRight - 它将父级向右对齐。
当您现在构建并运行应用程序时,它将产生以下输出屏幕 -
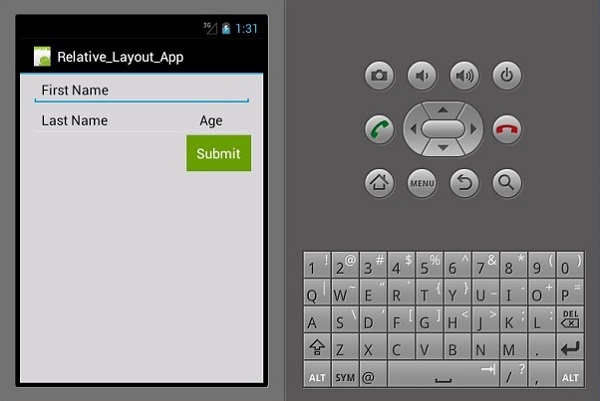
框架布局
框架布局用于仅显示一项。很难在此布局中排列多个项目而不使它们彼此重叠。
启动一个新项目并将其命名为frameLayoutApp。创建一个新的框架布局,如下所示。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<ImageView
android:id = "@+id/ImageView1"
android:scaleType = "matrix"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:src = "@drawable/img1" />
<TextView
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textSize = "50dp"
android:textColor = "#000"
android:text = "This is a Lake" />
<TextView
android:gravity = "right"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textSize = "50dp"
android:text = "A very Deep Lake"
android:layout_gravity = "bottom"
android:textColor = "#fff" />
</FrameLayout>
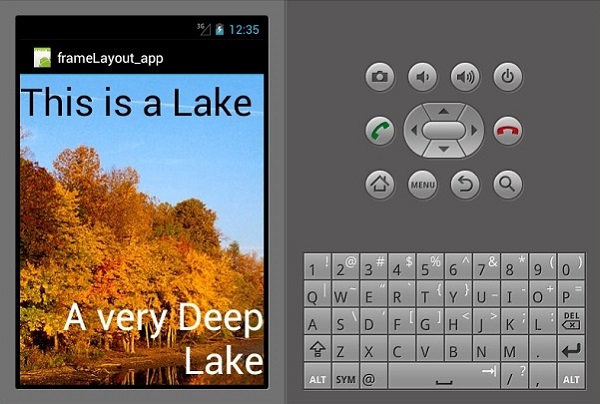
上面的代码创建了一个充满整个屏幕的imageView 。然后两个 textview 漂浮在imageView之上。
现在,构建并运行您的应用程序。它将显示以下输出 -
表格布局
在此布局中,视图按行和列排列。让我们看看它是如何工作的。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:stretchColumns = "1">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text = "First Name:"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<EditText
android:width = "100px"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "30dp"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text = "Last Name:"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<EditText
android:width = "50px"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "30dp"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text = "Residence:"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<EditText
android:width = "100px"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "30dp"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:text = "Occupation:"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<EditText
android:width = "100px"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "30dp"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text = "Cancel"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_margin = "10dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
<Button
android:text = "Submit"
android:width = "100px"
android:layout_margin = "10dp"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
上面的代码创建了一个使用table和rows排列的简单数据输入表单。
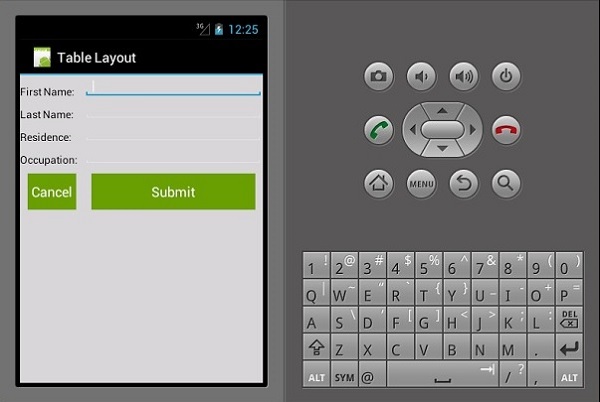
Xamarin - Android 小部件
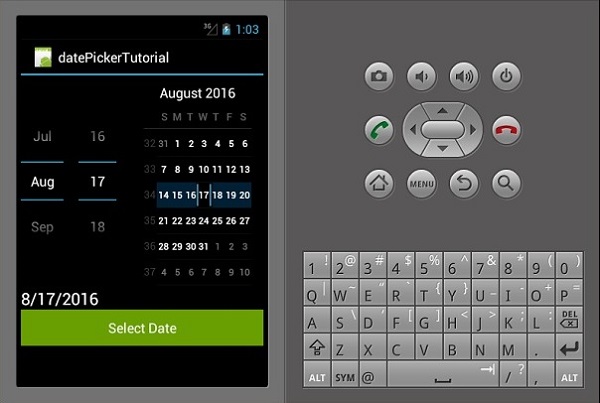
日期选择器
这是一个用于显示日期的小部件。在此示例中,我们将创建一个日期选择器,在文本视图上显示设置的日期。
首先,创建一个新项目并将其命名为datePickerExample。打开Main.axml并创建一个日期选择器、文本视图和一个按钮。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<DatePicker
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/datePicker1" />
<TextView
android:text = "Current Date"
android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/txtShowDate" />
<Button
android:text = "Select Date"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/btnSetDate" />
</LinearLayout>
接下来,转到Mainactivity.cs。我们首先在mainActivity:Activity类中创建一个文本视图的私有实例。
该实例将用于存储所选日期或默认日期。
private TextView showCurrentDate;
接下来,在setContentView()方法后添加以下代码。
DatePicker pickDate = FindViewById<DatePicker>(Resource.Id.datePicker1);
showCurrentDate = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.txtShowDate);
setCurrentDate();
Button button = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnSetDate);
button.Click += delegate {
showCurrentDate.Text = String.Format("{0}/{1}/{2}",
pickDate.Month, pickDate.DayOfMonth, pickDate.Year);
};
在上面的代码中,我们通过使用FindViewById类从main.axml文件中查找来引用日期选择器、文本视图和按钮。
引用后,我们设置按钮单击事件,该事件负责将所选日期从日期选择器传递到文本视图。
接下来,我们创建setCurrentDate()方法来向文本视图显示默认的当前日期。以下代码解释了它是如何完成的。
private void setCurrentDate() {
string TodaysDate = string.Format("{0}",
DateTime.Now.ToString("M/d/yyyy").PadLeft(2, '0'));
showCurrentDate.Text = TodaysDate;
}
DateTime.Now.ToString()类将今天的时间绑定到字符串对象。
现在,构建并运行应用程序。它应该显示以下输出 -
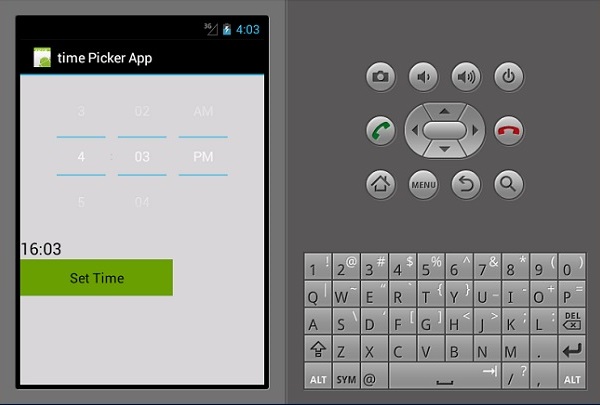
时间选择器
时间选择器是一个用于显示时间并允许用户选择和设置时间的小部件。我们将创建一个基本的时间选择器应用程序,用于显示时间并允许用户更改时间。
转到main.axml并添加新按钮、文本视图和时间选择器,如以下代码所示。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<TimePicker
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/timePicker1" />
<TextView
android:text = "Time"
android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/txt_showTime"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black" />
<Button
android:text = "Set Time"
android:layout_width = "200dp"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/btnSetTime"
android:textColor = "@android:color/black"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</LinearLayout>
转到MainActivity.cs添加在我们创建的文本视图上显示设置日期的功能。
public class MainActivity : Activity {
private TextView showCurrentTime;
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle) {
base.OnCreate(bundle);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
TimePicker Tpicker = FindViewById<TimePicker>(Resource.Id.timePicker1);
showCurrentTime = FindViewById<TextView>(Resource.Id.txt_showTime);
setCurrentTime();
Button button = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.btnSetTime);
button.Click += delegate {
showCurrentTime.Text = String.Format("{0}:{1}",
Tpicker.CurrentHour, Tpicker.CurrentMinute);
};
}
private void setCurrentTime() {
string time = string.Format("{0}",
DateTime.Now.ToString("HH:mm").PadLeft(2, '0'));
showCurrentTime.Text = time;
}
}
在上面的代码中,我们首先通过FindViewById<>类引用了timepicker、设置时间按钮和用于显示时间的 textview 。然后,我们为设置时间按钮创建了一个单击事件,单击该事件会将时间设置为用户选择的时间。默认情况下,它显示当前系统时间。
setCurrentTime ()方法类初始化txt_showTime文本视图以显示当前时间。
现在,构建并运行您的应用程序。它应该显示以下输出 -
旋转器
微调器是一个用于从一组选项中选择一个选项的小部件。它相当于下拉/组合框。首先,创建一个新项目并将其命名为Spinner App Tutorial。
打开布局文件夹下的Main.axml并创建一个新的spinner。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<Spinner
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/spinner1"
android:prompt = "@string/daysOfWeek" />
</LinearLayout>
打开位于值文件夹下的Strings.xml文件并添加以下代码以创建微调项目。
<resources>
<string name = "daysOfWeek">Choose a planet</string>
<string-array name = "days_array">
<item>Sunday</item>
<item>Monday</item>
<item>Tuesday</item>
<item>Wednesday</item>
<item>Thursday</item>
<item>Friday</item>
<item>Saturday</item>
<item>Sunday</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
接下来,打开MainActivity.cs添加显示一周中选定日期的功能。
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle) {
base.OnCreate(bundle);
// Set our view from the "main" layout resource
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
Spinner spinnerDays = FindViewById<Spinner>(Resource.Id.spinner1);
spinnerDays.ItemSelected += new EventHandler
<AdapterView.ItemSelectedEventArgs>(SelectedDay);
var adapter = ArrayAdapter.CreateFromResource(this,
Resource.Array.days_array, Android.Resource.Layout.SimpleSpinnerItem);
adapter.SetDropDownViewResource(Android.Resource.Layout.SimpleSpinnerDropD ownItem);
spinnerDays.Adapter = adapter;
}
private void SelectedDay(object sender, AdapterView.ItemSelectedEventArgs e) {
Spinner spinner = (Spinner)sender;
string toast = string.Format("The selected
day is {0}", spinner.GetItemAtPosition(e.Position));
Toast.MakeText(this, toast, ToastLength.Long).Show();
}
现在,构建并运行该应用程序。它应该显示以下输出 -
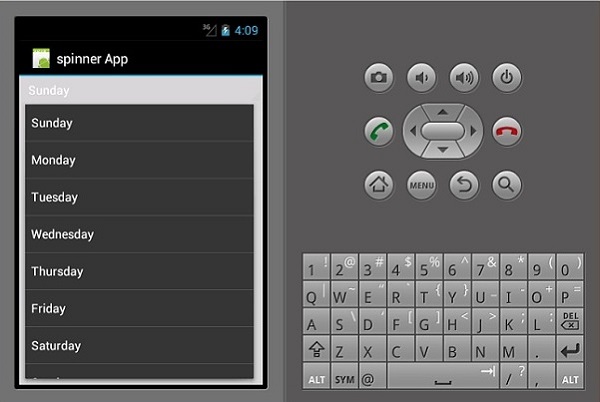
在上面的代码中,我们通过FindViewById<>类引用了在main.axml文件中创建的微调器。然后我们创建了一个新的arrayAdapter(),用于绑定strings.xml类中的数组项。
最后,我们创建了SelectedDay()方法,用于显示一周中选定的一天。
Xamarin - Android 对话框
警报对话框
在本节中,我们将创建一个按钮,单击该按钮会显示一个警报对话框。该对话框包含两个按钮,即“删除”和“取消”按钮。
首先,转到main.axml并在线性布局中创建一个新按钮,如以下代码所示。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:background = "#d3d3d3"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/MyButton"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Click to Delete"
android:textColor = "@android:color/background_dark"
android:background = "@android:color/holo_green_dark" />
</LinearLayout>
接下来,打开MainActivity.cs以创建警报对话框并添加其功能。
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle) {
base.OnCreate(bundle);
SetContentView(Resource.Layout.Main);
Button button = FindViewById<Button>(Resource.Id.MyButton);
button.Click += delegate {
AlertDialog.Builder alertDiag = new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
alertDiag.SetTitle("Confirm delete");
alertDiag.SetMessage("Once deleted the move cannot be undone");
alertDiag.SetPositiveButton("Delete", (senderAlert, args) => {
Toast.MakeText(this, "Deleted", ToastLength.Short).Show();
});
alertDiag.SetNegativeButton("Cancel", (senderAlert, args) => {
alertDiag.Dispose();
});
Dialog diag = alertDiag.Create();
diag.Show();
};
}
完成后,构建并运行您的应用程序以查看结果。
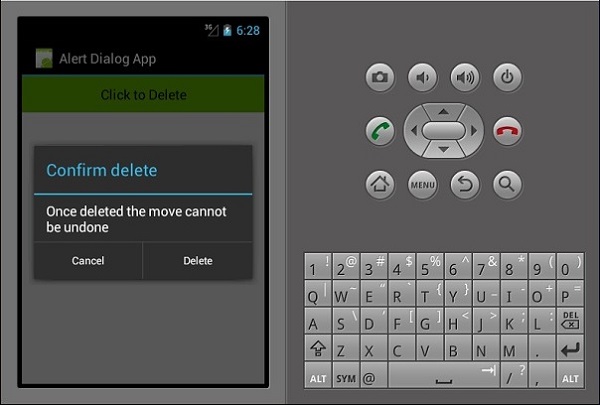
在上面的代码中,我们创建了一个名为alertDiag的警报对话框,其中包含以下两个按钮 -
setPositiveButton - 它包含“删除”按钮操作,单击该操作会显示一条确认消息“已删除”。
setNegativeButton - 它包含一个取消按钮,单击该按钮只会关闭警报对话框。
Xamarin - 画廊
图库是一种视图,用于显示水平可滚动列表中的项目。然后所选项目将显示在中心。在此示例中,您将创建一个包含可水平滚动的图像的图库。单击图像时将显示所选图像的编号。
首先,创建一个新项目并为其命名,例如Gallery App Tutorial。在开始编码之前,将 7 张图像粘贴到资源 /drawable 文件夹中。导航到资源文件夹下的main.axml以及线性布局标签之间的库。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#d3d3d3">
<Gallery
android:id="@+id/gallery"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
创建一个名为ImageAdapter的新类。此类将用于将图像绑定到我们上面创建的图库。
第一步是添加一个包含用于存储字段的上下文cont的类。
public class ImageAdapter : BaseAdapter {
Context cont;
public ImageAdapter(Context ct) {
cont = ct;
}
}
接下来,我们计算包含图像的数组列表并返回其大小。
public override int Count {
get {
return imageArraylist.Length;
}
}
在下一步中,我们获取该项目的位置。以下代码演示了如何执行此操作。
public override Java.Lang.Object GetItem(int position) {
return null;
}
p