
- 算法设计与分析
- 家
- 算法基础知识
- DAA - 简介
- DAA - 算法分析
- DAA-分析方法
- 渐近符号和先验分析
- 时间复杂度
- 马斯特定理
- DAA - 空间复杂性
- 分而治之
- DAA-分而治之
- DAA - 最大最小问题
- DAA-归并排序
- DAA-二分查找
- 施特拉森矩阵乘法
- 唐叶算法
- 河内塔
- 贪心算法
- DAA-贪婪法
- 旅行商问题
- Prim 的最小生成树
- 克鲁斯卡尔的最小生成树
- Dijkstra 的最短路径算法
- 地图着色算法
- DAA-分数背包
- DAA - 带截止日期的作业排序
- DAA - 最佳合并模式
- 动态规划
- DAA-动态规划
- 矩阵链乘法
- 弗洛伊德·沃歇尔算法
- DAA - 0-1 背包
- 最长公共子序列
- 旅行商问题| 动态规划
- 随机算法
- 随机算法
- 随机快速排序
- 卡格的最低削减
- 费舍尔-耶茨洗牌
- 近似算法
- 近似算法
- 顶点覆盖问题
- 设置封面问题
- 旅行推销员近似算法
- 排序技巧
- DAA-快速排序
- DAA-冒泡排序
- DAA——插入排序
- DAA-选择排序
- DAA——希尔排序
- DAA-堆排序
- DAA——桶排序
- DAA——计数排序
- DAA - 基数排序
- 搜索技巧
- 搜索技术介绍
- DAA - 线性搜索
- DAA-二分查找
- DAA - 插值搜索
- DAA - 跳转搜索
- DAA - 指数搜索
- DAA - 斐波那契搜索
- DAA - 子列表搜索
- DAA-哈希表
- 图论
- DAA-最短路径
- DAA - 多级图
- 最优成本二叉搜索树
- 堆算法
- DAA-二叉堆
- DAA-插入法
- DAA-Heapify 方法
- DAA-提取方法
- 复杂性理论
- 确定性计算与非确定性计算
- DAA-最大派系
- DAA - 顶点覆盖
- DAA - P 级和 NP 级
- DAA-库克定理
- NP 硬课程和 NP 完全课程
- DAA - 爬山算法
- DAA 有用资源
- DAA - 快速指南
- DAA - 有用的资源
- DAA - 讨论
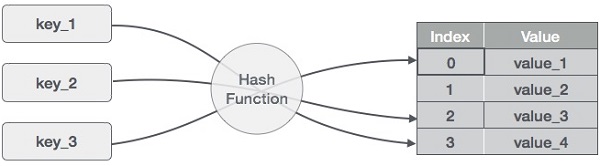
数据结构和算法 - 哈希表
哈希表是一种以关联方式存储数据的数据结构。在哈希表中,数据以数组格式存储,其中每个数据值都有自己唯一的索引值。如果我们知道所需数据的索引,数据访问就会变得非常快。
因此,它成为一种无论数据大小如何插入和搜索操作都非常快的数据结构。哈希表使用数组作为存储介质,并使用哈希技术生成要插入或定位元素的索引。
散列
散列是一种将一系列键值转换为一系列数组索引的技术。我们将使用模运算符来获取一系列键值。考虑一个大小为 20 的哈希表的示例,并且要存储以下项目。项目采用(键,值)格式。
- (1,20)
- (2,70)
- (42,80)
- (4,25)
- (12,44)
- (14,32)
- (17,11)
- (13,78)
- (37,98)
| 先生。 | 钥匙 | 哈希值 | 数组索引 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1%20=1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 % 20 = 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 42 | 42% 20 = 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 % 20 = 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 12 | 12% 20 = 12 | 12 |
| 6 | 14 | 14% 20 = 14 | 14 |
| 7 | 17 号 | 17% 20 = 17 | 17 号 |
| 8 | 13 | 13% 20 = 13 | 13 |
| 9 | 37 | 37% 20 = 17 | 17 号 |
线性探测
正如我们所看到的,哈希技术可能用于创建已使用的数组索引。在这种情况下,我们可以通过查找下一个单元格来搜索数组中的下一个空位置,直到找到空单元格。这种技术称为线性探测。
| 先生。 | 钥匙 | 哈希值 | 数组索引 | 线性探测后,数组索引 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1%20=1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 % 20 = 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 42 | 42% 20 = 2 | 2 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 | 4 % 20 = 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 12 | 12% 20 = 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 6 | 14 | 14% 20 = 14 | 14 | 14 |
| 7 | 17 号 | 17% 20 = 17 | 17 号 | 17 号 |
| 8 | 13 | 13% 20 = 13 | 13 | 13 |
| 9 | 37 | 37% 20 = 17 | 17 号 | 18 |
基本操作
以下是哈希表的基本主要操作。
搜索- 搜索哈希表中的元素。
插入- 在哈希表中插入一个元素。
delete - 从哈希表中删除一个元素。
数据项
定义一个具有一些数据和键的数据项,基于该数据项在哈希表中进行搜索。
struct DataItem {
int data;
int key;
};
哈希方法
定义一个哈希方法来计算数据项的键的哈希码。
int hashCode(int key){
return key % SIZE;
}
搜索操作
每当要搜索元素时,请计算传递的键的哈希码,并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位该元素。如果在计算的哈希码中未找到该元素,请使用线性探测来获取前面的元素。
struct DataItem *search(int key) {
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
例子
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10 // Define the size of the hash table
struct DataItem {
int key;
};
struct DataItem *hashArray[SIZE]; // Define the hash table as an array of DataItem pointers
int hashCode(int key) {
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE;
}
struct DataItem *search(int key) {
// get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// move in array until an empty slot is found or the key is found
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
// If the key is found, return the corresponding DataItem pointer
if (hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
// go to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// If the key is not found, return NULL
return NULL;
}
int main() {
// Initializing the hash table with some sample DataItems
struct DataItem item2 = {25}; // Assuming the key is 25
struct DataItem item3 = {64}; // Assuming the key is 64
struct DataItem item4 = {22}; // Assuming the key is 22
// Calculate the hash index for each item and place them in the hash table
int hashIndex2 = hashCode(item2.key);
hashArray[hashIndex2] = &item2;
int hashIndex3 = hashCode(item3.key);
hashArray[hashIndex3] = &item3;
int hashIndex4 = hashCode(item4.key);
hashArray[hashIndex4] = &item4;
// Call the search function to test it
int keyToSearch = 64; // The key to search for in the hash table
struct DataItem *result = search(keyToSearch);
if (result != NULL) {
printf("Key %d found, Value: %d\n", keyToSearch, result->key);
} else {
printf("Key %d not found.\n", keyToSearch);
}
return 0;
}
输出
Key 64 found, Value: 64
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
#define SIZE 10 // Define the size of the hash table
struct DataItem {
int key;
};
unordered_map<int, DataItem*> hashMap; // Define the hash table as an unordered_map
int hashCode(int key) {
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE;
}
DataItem* search(int key) {
// get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// move in the map until an empty slot is found or the key is found
while (hashMap[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
// If the key is found, return the corresponding DataItem pointer
if (hashMap[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashMap[hashIndex];
// go to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// If the key is not found, return nullptr
return nullptr;
}
int main() {
// Initializing the hash table with some sample DataItems
DataItem item2 = {25}; // Assuming the key is 25
DataItem item3 = {64}; // Assuming the key is 64
DataItem item4 = {22}; // Assuming the key is 22
// Calculate the hash index for each item and place them in the hash table
int hashIndex2 = hashCode(item2.key);
hashMap[hashIndex2] = &item2;
int hashIndex3 = hashCode(item3.key);
hashMap[hashIndex3] = &item3;
int hashIndex4 = hashCode(item4.key);
hashMap[hashIndex4] = &item4;
// Call the search function to test it
int keyToSearch = 64; // The key to search for in the hash table
DataItem* result = search(keyToSearch);
if (result != nullptr) {
cout << "Key " << keyToSearch << " found, Value: " << result->key << endl;
} else {
cout << "Key " << keyToSearch << " not found." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
Key 64 found, Value: 64
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
static final int SIZE = 10; // Define the size of the hash table
static class DataItem {
int key;
}
static HashMap<Integer, DataItem> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); // Define the hash table as a HashMap
static int hashCode(int key) {
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE;
}
static DataItem search(int key) {
// get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// move in map until an empty slot is found or the key is found
while (hashMap.get(hashIndex) != null) {
// If the key is found, return the corresponding DataItem
if (hashMap.get(hashIndex).key == key)
return hashMap.get(hashIndex);
// go to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// If the key is not found, return null
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initializing the hash table with some sample DataItems
DataItem item2 = new DataItem();
item2.key = 25; // Assuming the key is 25
DataItem item3 = new DataItem();
item3.key = 64; // Assuming the key is 64
DataItem item4 = new DataItem();
item4.key = 22; // Assuming the key is 22
// Calculate the hash index for each item and place them in the hash table
int hashIndex2 = hashCode(item2.key);
hashMap.put(hashIndex2, item2);
int hashIndex3 = hashCode(item3.key);
hashMap.put(hashIndex3, item3);
int hashIndex4 = hashCode(item4.key);
hashMap.put(hashIndex4, item4);
// Call the search function to test it
int keyToSearch = 64; // The key to search for in the hash table
DataItem result = search(keyToSearch);
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("Key " + keyToSearch + " found, Value: " + result.key);
} else {
System.out.println("Key " + keyToSearch + " not found.");
}
}
}
输出
Key 64 found, Value: 64
SIZE = 10 # Define the size of the hash table
class DataItem:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
hashMap = {} # Define the hash table as a dictionary
def hashCode(key):
# Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE
def search(key):
# get the hash
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
# move in map until an empty slot is found or the key is found
while hashIndex in hashMap:
# If the key is found, return the corresponding DataItem
if hashMap[hashIndex].key == key:
return hashMap[hashIndex]
# go to the next cell
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE
# If the key is not found, return None
return None
# Initializing the hash table with some sample DataItems
item2 = DataItem(25) # Assuming the key is 25
item3 = DataItem(64) # Assuming the key is 64
item4 = DataItem(22) # Assuming the key is 22
# Calculate the hash index for each item and place them in the hash table
hashIndex2 = hashCode(item2.key)
hashMap[hashIndex2] = item2
hashIndex3 = hashCode(item3.key)
hashMap[hashIndex3] = item3
hashIndex4 = hashCode(item4.key)
hashMap[hashIndex4] = item4
# Call the search function to test it
keyToSearch = 64 # The key to search for in the hash table
result = search(keyToSearch)
if result:
print(f"Key {keyToSearch} found, Value: {result.key}")
else:
print(f"Key {keyToSearch} not found.")
输出
Key 64 found, Value: 64
插入操作
每当要插入元素时,计算所传递的键的哈希码,并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位索引。如果在计算的哈希码处找到元素,则对空位置使用线性探测。
void insert(int key,int data) {
struct DataItem *item = (struct DataItem*) malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
item->data = data;
item->key = key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty or deleted cell
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL && hashArray[hashIndex]->key != -1) {
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
hashArray[hashIndex] = item;
}
例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 4 // Define the size of the hash table
struct DataItem {
int key;
};
struct DataItem *hashArray[SIZE]; // Define the hash table as an array of DataItem pointers
int hashCode(int key) {
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE;
}
void insert(int key) {
// Create a new DataItem using malloc
struct DataItem *newItem = (struct DataItem*)malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
if (newItem == NULL) {
// Check if malloc fails to allocate memory
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error\n");
return;
}
newItem->key = key;
// Initialize other data members if needed
// Calculate the hash index for the key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// Handle collisions (linear probing)
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
// Move to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = newItem;
}
int main() {
// Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(42); // Insert an item with key 42
insert(25); // Insert an item with key 25
insert(64); // Insert an item with key 64
insert(22); // Insert an item with key 22
// Output the populated hash table
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != NULL) {
printf("Index %d: Key %d\n", i, hashArray[i]->key);
} else {
printf("Index %d: Empty\n", i);
}
}
return 0;
}
输出
Index 0: Key 64 Index 1: Key 25 Index 2: Key 42 Index 3: Key 22
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define SIZE 4 // Define the size of the hash table
struct DataItem {
int key;
};
std::vector<DataItem*> hashArray(SIZE, nullptr); // Define the hash table as a vector of DataItem pointers
int hashCode(int key)
{
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE;
}
void insert(int key)
{
// Create a new DataItem using new (dynamic memory allocation)
DataItem *newItem = new DataItem;
newItem->key = key;
// Initialize other data members if needed
// Calculate the hash index for the key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// Handle collisions (linear probing)
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
// Move to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = newItem;
}
int main()
{
// Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(42); // Insert an item with key 42
insert(25); // Insert an item with key 25
insert(64); // Insert an item with key 64
insert(22); // Insert an item with key 22
// Output the populated hash table
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != nullptr) {
std::cout << "Index " << i << ": Key " << hashArray[i]->key << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Index " << i << ": Empty" << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
输出
Index 0: Key 64 Index 1: Key 25 Index 2: Key 42 Index 3: Key 22
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
static final int SIZE = 4; // Define the size of the hash table
static class DataItem {
int key;
}
static DataItem[] hashArray = new DataItem[SIZE]; // Define the hash table as an array of DataItem pointers
static int hashCode(int key) {
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE;
}
static void insert(int key) {
// Create a new DataItem
DataItem newItem = new DataItem();
newItem.key = key;
// Initialize other data members if needed
// Calculate the hash index for the key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// Handle collisions (linear probing)
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != null) {
// Move to the next cell
hashIndex++;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = newItem;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(42); // Insert an item with key 42
insert(25); // Insert an item with key 25
insert(64); // Insert an item with key 64
insert(22); // Insert an item with key 22
// Output the populated hash table
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != null) {
System.out.println("Index " + i + ": Key " + hashArray[i].key);
} else {
System.out.println("Index " + i + ": Empty");
}
}
}
}
输出
Index 0: Key 64 Index 1: Key 25 Index 2: Key 42 Index 3: Key 22
SIZE = 4 # Define the size of the hash table
class DataItem:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
hashArray = [None] * SIZE # Define the hash table as a list of DataItem pointers
def hashCode(key):
# Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE
def insert(key):
# Create a new DataItem
newItem = DataItem(key)
# Initialize other data members if needed
# Calculate the hash index for the key
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
# Handle collisions (linear probing)
while hashArray[hashIndex] is not None:
# Move to the next cell
hashIndex += 1
# Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE
# Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = newItem
# Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(42) # Insert an item with key 42
insert(25) # Insert an item with key 25
insert(64) # Insert an item with key 64
insert(22) # Insert an item with key 22
# Output the populated hash table
for i in range(SIZE):
if hashArray[i] is not None:
print(f"Index {i}: Key {hashArray[i].key}")
else:
print(f"Index {i}: Empty")
输出
Index 0: Key 64 Index 1: Key 25 Index 2: Key 42 Index 3: Key 22
删除操作
每当要删除一个元素时,计算所传递的键的哈希码,并使用该哈希码作为数组中的索引来定位索引。如果在计算的哈希码中未找到元素,请使用线性探测来获取前面的元素。找到后,将虚拟项存储在那里以保持哈希表的性能完好无损。
struct DataItem* delete(struct DataItem* item) {
int key = item->key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] !=NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
struct DataItem* temp = hashArray[hashIndex];
//assign a dummy item at deleted position
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem;
return temp;
}
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 5 // Define the size of the hash table
struct DataItem {
int key;
};
struct DataItem *hashArray[SIZE]; // Define the hash table as an array of DataItem pointers
int hashCode(int key) {
// Implement your hash function here
// Return a hash value based on the key
}
void insert(int key) {
// Create a new DataItem using malloc
struct DataItem *newItem = (struct DataItem*)malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
if (newItem == NULL) {
// Check if malloc fails to allocate memory
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation error\n");
return;
}
newItem->key = key;
// Initialize other data members if needed
// Calculate the hash index for the key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// Handle collisions (linear probing)
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
// Move to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = newItem;
// Print the inserted item's key and hash index
printf("Inserted key %d at index %d\n", newItem->key, hashIndex);
}
void delete(int key) {
// Find the item in the hash table
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
// Mark the item as deleted (optional: free memory)
free(hashArray[hashIndex]);
hashArray[hashIndex] = NULL;
// Print the deleted item's key and hash index
printf("Deleted key %d at index %d\n", key, hashIndex);
return;
}
// Move to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// If the key is not found, print a message
printf("Item with key %d not found.\n", key);
}
int main() {
// Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(1); // Insert an item with key 42
insert(2); // Insert an item with key 25
insert(3); // Insert an item with key 64
insert(4); // Insert an item with key 22
delete(2); // Delete an item with key 42
delete(4); // Delete an item with key 25
// Print the hash table's contents after delete operations
printf("Hash Table Contents:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != NULL) {
printf("Index %d: Key %d\n", i, hashArray[i]->key);
} else {
printf("Index %d: Empty\n", i);
}
}
return 0;
}
输出
Inserted key 1 at index 1 Inserted key 2 at index 2 Inserted key 3 at index 3 Inserted key 4 at index 4 Deleted key 2 at index 2 Deleted key 4 at index 4 Hash Table Contents: Index 0: Empty Index 1: Key 1 Index 2: Empty Index 3: Key 3 Index 4: Empty
#include <iostream>
const int SIZE = 5; // Define the size of the hash table
struct DataItem {
int key;
};
struct DataItem* hashArray[SIZE]; // Define the hash table as an array of DataItem pointers
int hashCode(int key) {
// Implement your hash function here
// Return a hash value based on the key
// A simple hash function (modulo division)
return key % SIZE;
}
void insert(int key) {
// Create a new DataItem using new
struct DataItem* newItem = new DataItem;
newItem->key = key;
// Initialize other data members if needed
// Calculate the hash index for the key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// Handle collisions (linear probing)
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
// Move to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = newItem;
// Print the inserted item's key and hash index
std::cout << "Inserted key " << newItem->key << " at index " << hashIndex << std::endl;
}
void deleteItem(int key) {
// Find the item in the hash table
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
// Mark the item as deleted (optional: free memory)
delete hashArray[hashIndex];
hashArray[hashIndex] = nullptr;
// Print the deleted item's key and hash index
std::cout << "Deleted key " << key << " at index " << hashIndex << std::endl;
return;
}
// Move to the next cell
++hashIndex;
// Wrap around the table if needed
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
// If the key is not found, print a message
std::cout << "Item with key " << key << " not found." << std::endl;
}
int main() {
// Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(1); // Insert an item with key 42
insert(2); // Insert an item with key 25
insert(3); // Insert an item with key 64
insert(4); // Insert an item with key 22
deleteItem(2); // Delete an item with key 42
deleteItem(4); // Delete an item with key 25
// Print the hash table's contents after delete operations
std::cout << "Hash Table Contents:" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != nullptr) {
std::cout << "Index " << i << ": Key " << hashArray[i]->key << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Index " << i << ": Empty" << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
输出
Inserted key 1 at index 1 Inserted key 2 at index 2 Inserted key 3 at index 3 Inserted key 4 at index 4 Deleted key 2 at index 2 Deleted key 4 at index 4 Hash Table Contents: Index 0: Empty Index 1: Key 1 Index 2: Empty Index 3: Key 3 Index 4: Empty
public class Main {
static final int SIZE = 5; // Define the size of the hash table
static class DataItem {
int key;
DataItem(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
static DataItem[] hashArray = new DataItem[SIZE]; // Define the hash table as an array of DataItem objects
static int hashCode(int key) {
// Implement your hash function here
// Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE; // A simple hash function using modulo operator
}
static void insert(int key) {
// Calculate the hash index for the key
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
// Handle collisions (linear probing)
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != null) {
// Move to the next cell
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
// Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = new DataItem(key);
// Print the inserted item's key and hash index
System.out.println("Inserted key " + key + " at index " + hashIndex);
}
static void delete(int key) {
// Find the item in the hash table
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != null) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex].key == key) {
// Mark the item as deleted (optional: free memory)
hashArray[hashIndex] = null;
// Print the deleted item's key and hash index
System.out.println("Deleted key " + key + " at index " + hashIndex);
return;
}
// Move to the next cell
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
// If the key is not found, print a message
System.out.println("Item with key " + key + " not found.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(1); // Insert an item with key 1
insert(2); // Insert an item with key 2
insert(3); // Insert an item with key 3
insert(4); // Insert an item with key 4
delete(2); // Delete an item with key 2
delete(4); // Delete an item with key 4
// Print the hash table's contents after delete operations
System.out.println("Hash Table Contents:");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != null) {
System.out.println("Index " + i + ": Key " + hashArray[i].key);
} else {
System.out.println("Index " + i + ": Empty");
}
}
}
}
输出
Inserted key 1 at index 1 Inserted key 2 at index 2 Inserted key 3 at index 3 Inserted key 4 at index 4 Deleted key 2 at index 2 Deleted key 4 at index 4 Hash Table Contents: Index 0: Empty Index 1: Key 1 Index 2: Empty Index 3: Key 3 Index 4: Empty
SIZE = 5 # Define the size of the hash table
class DataItem:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
def hashCode(key):
# Implement your hash function here
# Return a hash value based on the key
return key % SIZE
def insert(key):
global hashArray # Access the global hashArray variable
# Calculate the hash index for the key
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
# Handle collisions (linear probing)
while hashArray[hashIndex] is not None:
# Move to the next cell
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE
# Insert the new DataItem at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = DataItem(key)
# Print the inserted item's key and hash index
print(f"Inserted key {key} at index {hashIndex}")
def delete(key):
global hashArray # Access the global hashArray variable
# Find the item in the hash table
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
while hashArray[hashIndex] is not None:
if hashArray[hashIndex].key == key:
# Mark the item as deleted (optional: free memory)
hashArray[hashIndex] = None
# Print the deleted item's key and hash index
print(f"Deleted key {key} at index {hashIndex}")
return
# Move to the next cell
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE
# If the key is not found, print a message
print(f"Item with key {key} not found.")
# Initialize the hash table as a list of None values
hashArray = [None] * SIZE
# Call the insert function with different keys to populate the hash table
insert(1) # Insert an item with key 1
insert(2) # Insert an item with key 2
insert(3) # Insert an item with key 3
insert(4) # Insert an item with key 4
delete(2) # Delete an item with key 2
delete(4) # Delete an item with key 4
# Print the hash table's contents after delete operations
print("Hash Table Contents:")
for i in range(SIZE):
if hashArray[i] is not None:
print(f"Index {i}: Key {hashArray[i].key}")
else:
print(f"Index {i}: Empty")
输出
Inserted key 1 at index 1 Inserted key 2 at index 2 Inserted key 3 at index 3 Inserted key 4 at index 4 Deleted key 2 at index 2 Deleted key 4 at index 4 Hash Table Contents: Index 0: Empty Index 1: Key 1 Index 2: Empty Index 3: Key 3 Index 4: Empty
完成实施
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define SIZE 20
struct DataItem {
int data;
int key;
};
struct DataItem* hashArray[SIZE];
struct DataItem* dummyItem;
struct DataItem* item;
int hashCode(int key) {
return key % SIZE;
}
struct DataItem *search(int key) {
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
void insert(int key,int data) {
struct DataItem *item = (struct DataItem*) malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
item->data = data;
item->key = key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty or deleted cell
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL && hashArray[hashIndex]->key != -1) {
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
hashArray[hashIndex] = item;
}
struct DataItem* delete(struct DataItem* item) {
int key = item->key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while(hashArray[hashIndex] != NULL) {
if(hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
struct DataItem* temp = hashArray[hashIndex];
//assign a dummy item at deleted position
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem;
return temp;
}
//go to next cell
++hashIndex;
//wrap around the table
hashIndex %= SIZE;
}
return NULL;
}
void display() {
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i<SIZE; i++) {
if(hashArray[i] != NULL)
printf(" (%d,%d)",hashArray[i]->key,hashArray[i]->data);
else
printf(" ~~ ");
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
dummyItem = (struct DataItem*) malloc(sizeof(struct DataItem));
dummyItem->data = -1;
dummyItem->key = -1;
insert(1, 20);
insert(2, 70);
insert(42, 80);
insert(4, 25);
insert(12, 44);
insert(14, 32);
insert(17, 11);
insert(13, 78);
insert(37, 97);
display();
item = search(37);
if(item != NULL) {
printf("Element found: %d\n", item->data);
} else {
printf("Element not found\n");
}
delete(item);
item = search(37);
if(item != NULL) {
printf("Element found: %d\n", item->data);
} else {
printf("Element not found\n");
}
}
输出
~~ (1, 20) (2, 70) (42, 80) (4, 25) ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ (12, 44) (13, 78) (14, 32) ~~ ~~ (17, 11) (37, 97) ~~ Element found: 97 Element not found
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define SIZE 20
struct DataItem {
int data;
int key;
};
std::vector<DataItem*> hashArray(SIZE, nullptr);
DataItem* dummyItem;
DataItem* item;
int hashCode(int key) {
return key % SIZE;
}
DataItem* search(int key) {
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
//go to next cell
//wrap around the table
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
return nullptr;
}
void insert(int key, int data) {
DataItem* item = new DataItem;
item->data = data;
item->key = key;
//get the hash
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
//move in array until an empty or deleted cell
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != nullptr && hashArray[hashIndex]->key != -1) {
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
hashArray[hashIndex] = item;
}
DataItem* deleteItem(DataItem* item) {
int key = item->key;
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != nullptr) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex]->key == key) {
DataItem* temp = hashArray[hashIndex];
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem;
return temp;
}
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
return nullptr;
}
void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != nullptr)
std::cout << " (" << hashArray[i]->key << "," << hashArray[i]->data << ")";
else
std::cout << " ~~ ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
int main() {
dummyItem = new DataItem;
dummyItem->data = -1;
dummyItem->key = -1;
insert(1, 20);
insert(2, 70);
insert(42, 80);
insert(4, 25);
insert(12, 44);
insert(14, 32);
insert(17, 11);
insert(13, 78);
insert(37, 97);
display();
item = search(37);
if (item != nullptr) {
std::cout << "Element found: " << item->data << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl;
}
// Clean up allocated memory
delete(item);
item = search(37);
if (item != nullptr) {
std::cout << "Element found: " << item->data << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Element not found" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
~~ (1, 20) (2, 70) (42, 80) (4, 25) ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ (12, 44) (13, 78) (14, 32) ~~ ~~ (17, 11) (37, 97) ~~ Element found: 97 Element not found
public class HashTableExample {
static final int SIZE = 20;
static class DataItem {
int data;
int key;
DataItem(int data, int key) {
this.data = data;
this.key = key;
}
}
static DataItem[] hashArray = new DataItem[SIZE];
static DataItem dummyItem = new DataItem(-1, -1);
static DataItem item;
static int hashCode(int key) {
return key % SIZE;
}
static DataItem search(int key) {
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != null) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex].key == key)
return hashArray[hashIndex];
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
return null;
}
static void insert(int key, int data) {
DataItem item = new DataItem(data, key);
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != null && hashArray[hashIndex].key != -1) {
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
hashArray[hashIndex] = item;
}
static DataItem deleteItem(DataItem item) {
int key = item.key;
int hashIndex = hashCode(key);
while (hashArray[hashIndex] != null) {
if (hashArray[hashIndex].key == key) {
DataItem temp = hashArray[hashIndex];
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem;
return temp;
}
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE;
}
return null;
}
static void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++) {
if (hashArray[i] != null)
System.out.print(" (" + hashArray[i].key + "," + hashArray[i].data + ")");
else
System.out.print(" ~~ ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insert(1, 20);
insert(2, 70);
insert(42, 80);
insert(4, 25);
insert(12, 44);
insert(14, 32);
insert(17, 11);
insert(13, 78);
insert(37, 97);
display();
item = search(37);
if (item != null) {
System.out.println("Element found: " + item.data);
} else {
System.out.println("Element not found");
}
deleteItem(item);
item = search(37);
if (item != null) {
System.out.println("Element found: " + item.data);
} else {
System.out.println("Element not found");
}
}
}
输出
~~ (1, 20) (2, 70) (42, 80) (4, 25) ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ (12, 44) (13, 78) (14, 32) ~~ ~~ (17, 11) (37, 97) ~~ Element found: 97 Element not found
SIZE = 20
class DataItem:
def __init__(self, data, key):
self.data = data
self.key = key
# Initialize the hash array with None values
hashArray = [None] * SIZE
# Create a dummy item to mark deleted cells in the hash table
dummyItem = DataItem(-1, -1)
# Variable to hold the item found in the search operation
item = None
# Hash function to calculate the hash index for the given key
def hashCode(key):
return key % SIZE
# Function to search for an item in the hash table by its key
def search(key):
# Calculate the hash index using the hash function
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
# Traverse the array until an empty cell is encountered
while hashArray[hashIndex] is not None:
if hashArray[hashIndex].key == key:
# Item found, return the item
return hashArray[hashIndex]
# Move to the next cell (linear probing)
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE
# If the loop terminates without finding the item, it means the item is not present
return None
# Function to insert an item into the hash table
def insert(key, data):
# Create a new DataItem object
item = DataItem(data, key)
# Calculate the hash index using the hash function
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
# Handle collisions using linear probing (move to the next cell until an empty cell is found)
while hashArray[hashIndex] is not None and hashArray[hashIndex].key != -1:
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE
# Insert the item into the hash table at the calculated index
hashArray[hashIndex] = item
# Function to delete an item from the hash table
def deleteItem(item):
key = item.key
# Calculate the hash index using the hash function
hashIndex = hashCode(key)
# Traverse the array until an empty or deleted cell is encountered
while hashArray[hashIndex] is not None:
if hashArray[hashIndex].key == key:
# Item found, mark the cell as deleted by replacing it with the dummyItem
temp = hashArray[hashIndex]
hashArray[hashIndex] = dummyItem
return temp
# Move to the next cell (linear probing)
hashIndex = (hashIndex + 1) % SIZE
# If the loop terminates without finding the item, it means the item is not present
return None
# Function to display the hash table
def display():
for i in range(SIZE):
if hashArray[i] is not None:
# Print the key and data of the item at the current index
print(" ({}, {})".format(hashArray[i].key, hashArray[i].data), end="")
else:
# Print ~~ for an empty cell
print(" ~~ ", end="")
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Test the hash table implementation
# Insert some items into the hash table
insert(1, 20)
insert(2, 70)
insert(42, 80)
insert(4, 25)
insert(12, 44)
insert(14, 32)
insert(17, 11)
insert(13, 78)
insert(37, 97)
# Display the hash table
display()
# Search for an item with a specific key (37)
item = search(37)
# Check if the item was found or not and print the result
if item is not None:
print("Element found:", item.data)
else:
print("Element not found")
# Delete the item with key 37 from the hash table
deleteItem(item)
# Search again for the item with key 37 after deletion
item = search(37)
# Check if the item was found or not and print the result
if item is not None:
print("Element found:", item.data)
else:
print("Element not found")
输出
~~ (1, 20) (2, 70) (42, 80) (4, 25) ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ ~~ (12, 44) (13, 78) (14, 32) ~~ ~~ (17, 11) (37, 97) ~~ Element found: 97 Element not found